In our recent CMMC webinar, we joined forces with Vanta and A-LIGN to discuss the updated CMMC 2.0 and what organizations should be doing now to meet the requirements. Morgan Kaplan, Director of USG Strategy & Affairs at Vanta, moderated a lively discussion between Metin Kortak, Rhymetec CISO, and Matt Bruggeman, Director of Federal Sales at A-LIGN.
This Rhymetec CMMC Compliance Checklist for CMMC Level 2 is directly based on their discussion and pulls in expert insights from the webinar. Check out the recording of the full webinar here.

First, What Is CMMC?
CMMC, or the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification, is the Department of Defense's approach to standardizing cybersecurity requirements across its supply chain. It protects Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) by requiring contractors (and many subcontractors as well) to meet security practices based on the type of work and data they handle.
As Rhymetec CISO Metin Kortak explained in our webinar:
"CMMC is a framework that's been developed by the US Department of Defense, and it really applies to anyone who's working with the Department of Defense and also processes, transmits, or stores controlled unclassified information. If you're processing that information and you're also working on direct contracts with the Department of Defense, or if you're one of their subcontractors, that means CMMC might apply to you." - Metin Kortak, CISO at Rhymetec
That scope includes contractors, manufacturers, software vendors, and cloud service providers that deal with DoD contracts even indirectly. This Rhymetec CMMC Compliance Checklist breaks down what's required and how to build a roadmap that aligns with contract timelines for CMMC Level 2. (If you need CMMC Level 1, check out our CMMC Level 1 Checklist).
You can also contact our team today and we'd be happy to walk you through everything you need to know.
Contact
How Does The Updated CMMC Version 2.0 Differ From The Original Version 1.0?
CMMC 2.0 simplifies the framework while reinforcing its core goal to protect sensitive data within the Defense Industrial Base (DIB). The shift from Version 1.0 to 2.0 reflects feedback from industry stakeholders who found the original model extremely onerous to implement:
"CMMC 1.0 was quite strict and required organizations to go through many additional requirements outside of NIST 800-171. This made the process extremely difficult, especially for organizations that need to comply with other government compliance frameworks such as FedRAMP. Based on the feedback received, 2.0 is a less strict version of CMMC, while still maintaining the core security requirements.” - Metin Kortak, CISO at Rhymetec
CMMC 1.0 introduced five maturity levels and included additional practices and documentation beyond NIST 800-171. This generated a lot of confusion for subcontractors and SaaS providers, especially those also working toward FedRAMP.
CMMC 2.0 successfully restructured the model around three levels and removed the unique CMMC-only requirements. The new version falls under basic safeguarding practices and are derived from the Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) 52.204-21, which directly references and relates to NIST SP 800-171 as part of its requirements.
This change reduces redundancy and increases compatibility with other federal frameworks. With the updated version, CMMC consultants have seen renewed customer interest:
"In the past, in terms of the requirements themselves, it's been more around NIST 800-171, plus a couple of other CMMC requirements. Recently, there have been updates to the CMMC framework. They've updated from Version 1.0 to 2.0. We've seen a lot of interest from our customers about this new version of CMMC." - Metin Kortak, CISO at Rhymetec
This renewed interest is likely since the assessment requirements have evolved. The new version maintains some elements of the previous requirements, but refines the role of C3PAOs (Certified Third Party Assessor Organizations):
"C3PAOs come in and assess you against the requirements, depending on the level that you're at. Our goal is to validate that the sensitive data is actually being protected, because looking historically at just relying on self-attestations to 800-171 for anybody within the supply chain has not been sufficient." - Matt Bruggeman, A-LIGN
In short, CMMC 2.0 is:
- Better aligned with existing industry standards.
- Highly adaptable to real-world constraints.
- More accessible for businesses supporting DoD missions.
Getting Started: Determining Which Level You Need and A Gap Assessment
Before you get started on working through your CMMC compliance checklist (for whichever level you need), it’s important to understand what type of data your organization handles.
This will determine which certification level of CMMC applies to your business:
"The first thing is understanding what type of data you process. If you don't know that, working with a partner to help you determine that can be helpful, because that's going to help you figure out which level of compliance you're going to need to do for CMMC." - Metin Kortak, CISO at Rhymetec
Determining Which Type of Organization Your Organization Handles
Two main types of information matter when it comes to CMMC:
- Federal Contract Information (FCI): Any information provided by or generated for the government under a contract that’s not intended for public release. Include project timelines, internal communications, and organizational charts related to a DoD contract.
- Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI): More sensitive than FCI. This is information that the government has decided needs to be protected, but doesn’t meet classification levels such as “Secret” or “Top Secret”:
“CUI is sensitive information that does not meet the criteria for classification but must still be protected. It is Government-created or owned UNCLASSIFIED information that allows for, or requires, safeguarding and dissemination controls in accordance with laws, regulations, or Government-wide policies.” - Department of Defense
Examples of CUI include software code related to defense programs, incident response reports, training content, documentation for DoD systems, and API guides that define how systems interoperate with DoD environments.
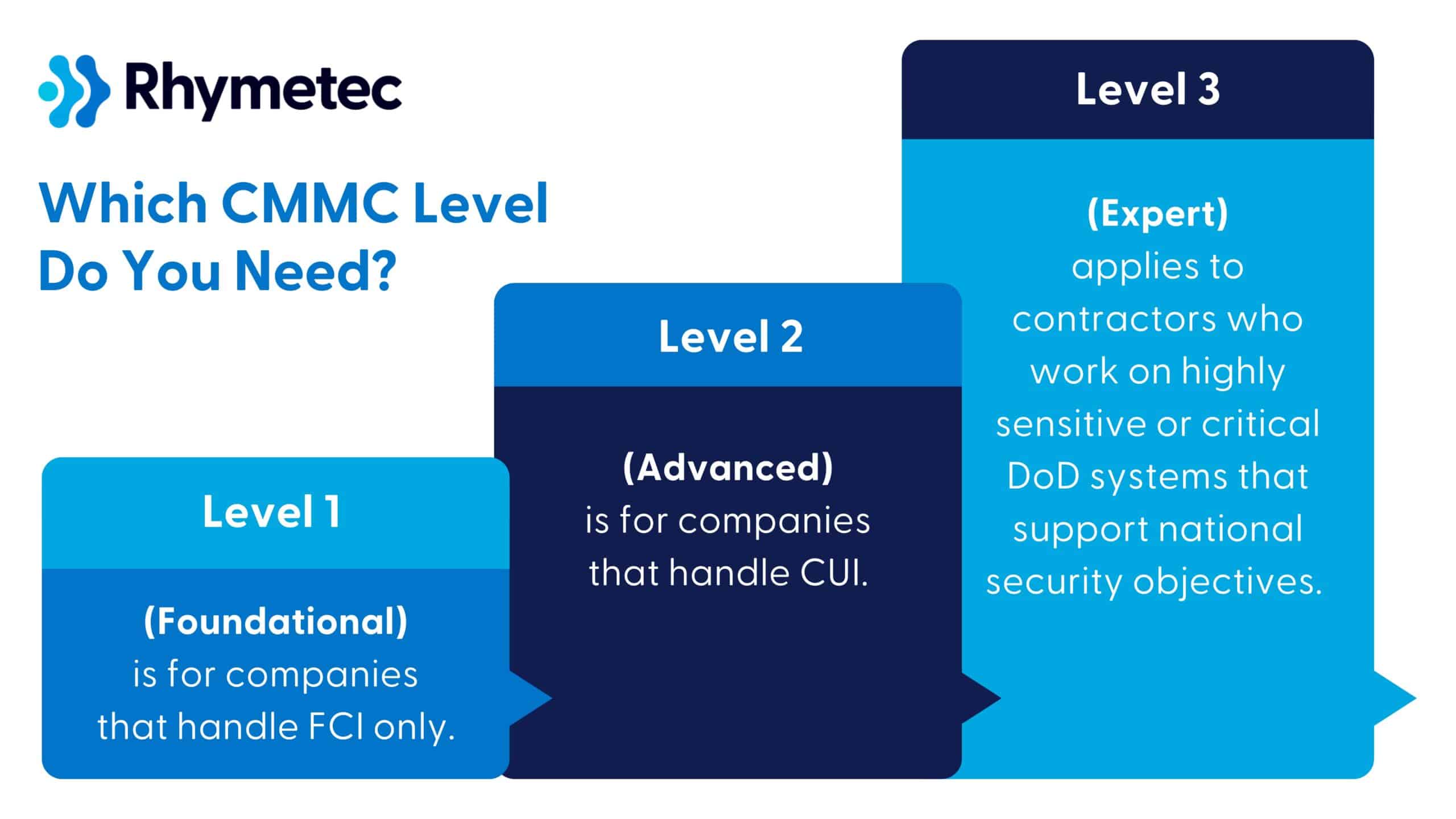
So, which CMMC Level Do You Need?
Based on the type of data your organization handles, there are three levels of CMMC:
- Level 1 (Foundational) applies to companies that handle FCI only and do not store or process any CUI. This could be an IT helpdesk vendor managing onboarding for non-sensitive systems, construction companies that work on DoD facilities, or a staffing agency that places civilian contractors on DoD projects, just to give a few examples. The new version of Level 1 falls under basic safeguarding practices and is derived from the Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) 52.204-21, which directly references and relates to NIST SP 800-171 as part of its requirements.
- Level 2 (Advanced) is for companies that handle CUI. Examples include a SaaS provider offering workflow tools to a DoD agency that handles technical mission data, manufacturing companies that produce parts for defense blueprints, and subcontractors who write embedded software for military systems. Requirements entail full implementation of NIST SP 800-171 (110 controls). Some contractors allow self-attestation, but many require a C3PAO to perform an audit and issue your certification.
- Level 3 (Expert) applies to contractors who work on highly sensitive or critical DoD systems that support national security objectives. Defense contractors managing secure communications infrastructure, and aerospace or defense firms involved in weapons systems development, are examples of organizations that will need Level 3. Requirements include more advanced security controls based on NIST SP 800-172, and a government-led assessment must be conducted.
Getting Started: Conducting A Gap Assessment
Once you’ve identified which level applies to your organization, the next step is a gap assessment.
"For the next step, at Rhymetec, we always start with a gap assessment. A gap assessment against the NIST 800-171 controls is a must-have…It helps you determine if you have any missing controls or if you have any gaps in your compliance, so you can start putting together a roadmap for completing the remaining controls." - Metin Kortak, CISO at Rhymetec
The aim is to compare your current environment against the required controls. This process tells you what needs to be done before you’re ready to self-attest or move into the certification phase.
CMMC 2.0 also allows you to use a Plan of Action and Milestones (POA&M) to formally track missing controls and your plan for implementing them:
“In 2.0, CMMC came out with a final action and milestones plan. This document essentially allows you to create implementation plans for controls that are missing in your gap assessment, so that you can remediate these controls within a certain amount of time. This is also something you can work with third parties on or conduct your own self-assessment.” - Metin Kortak, CISO at Rhymetec
Next, we'll break down what you need to do for each level of CMMC:
CMMC Compliance Checklist: What Are The Level 2 Requirements?
CMMC Level 2 applies to organizations that process, store, or transmit CUI as part of their work with the Department of Defense. This includes software vendors, MSPs, and subcontractors that handle technical data, system specifications, or any other sensitive project-related information:
"If you process CUI as part of your work in the supply chain of the DoD, that's where the Level 2 requirements come in. A majority of organizations that handle CUI will require a third-party audit and CMMC certification." - Matt Bruggeman, A-LIGN
Level 2 is based on the controls in NIST SP 800-171.
These controls are grouped into areas to include access control, configuration management, incident response, and audit and accountability. For a more comprehensive list of the 110 controls (with more technical detail), see the NIST SP 800-171 official documentation here.
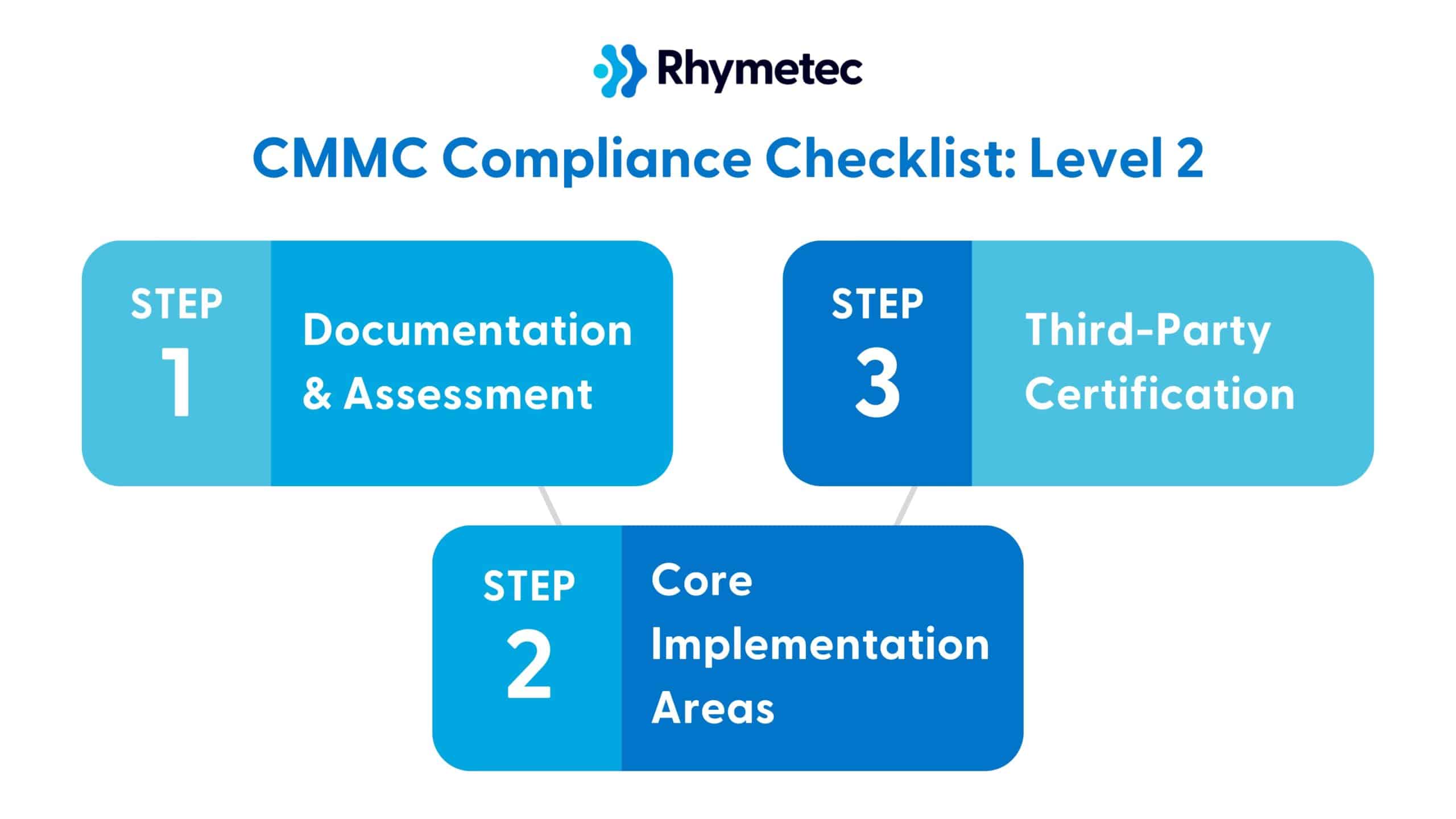
Below is a checklist with the main items broken down into three categories to give you an idea of what to expect:
1. Documentation and Assessment
Complete a full NIST 800- 171A self-assessment (or third-party assessment).
This will show which controls your organization is missing or needs to improve, and form the foundation for remediation work needed for CMMC.
Develop a System Security Plan (SSP).
The SSP documents how your organization has implemented each NIST control and serves as the core evidence package when it comes time for your external assessment by a C3PAO.
Create a Plan of Action and Milestones (POA&M) for any discovered gaps.
The purpose of a POA&M is to outline the timelines and resources needed to remediate security control deficiencies you discovered during the self-assessment.
Submit or update your SPRS score.
The Supplier Performance Risk System (SPRS) score is an indication of how many of the 110 controls you've implemented, and is required by DoD contracting officers when evaluating vendor eligibility.
Document CUI data flows.
Mapping how CUI moves through your systems (and your vendors) is a core part of scoping your security boundary and making sure this is documented in your compliance program.
2. Core Implementation Areas
Access Control.
Enforce measures to include least privilege and MFA, and manage privileged accounts.
Asset Management.
Inventory CUI systems, segment networks, and label systems appropriately.
Audit and Accountability.
Retain records and review logs for anomalies.
Configuration Management.
Establish secure baseline configurations and change control procedures.
Identification and Authentication.
Make sure your organization is using strong authentication mechanisms and unique IDs for users.
Incident Response.
Create an incident response plan if your organization doesn't already have one, and test it.
Maintenance.
Track system maintenance activities.
Media Protection.
Create policies to limit and monitor removable media and sanitize storage before reuse.
Personnel Security.
Screen employees, terminate access promptly, and deliver regular security training.
Physical Protection.
Restrict physical access to systems and facilities handling CUI.
Risk Assessments.
Perform risk assessments and remediate vulnerabilities.
Security Assessment.
Conduct internal control testing and prepare for external audits.
System and Communications Protection.
Implement boundary defenses and encryption for CUI in transit.
System and Information Integrity.
Deploy measures to include endpoint protection, monitoring for malware, and regular patching.
3. Third-Party Certification
Most organizations at Level 2 will be required to undergo an audit by a CMMC Third Party Assessment Organization (C3PAO).
Some contractors (specifically, those working on lower-risk programs) might be permitted to self-attest for Level 2, but this is an exception.
C3PAOs validate the implementation of the 110 controls. Generally, you can expect them to conduct technical testing, interview your staff, and verify documentation.
Preparing for Level 2 requires an enormous amount of coordinated effort across technical and operational domains. Working with a CMMC Consultant can vastly streamline the process for you.
CMMC Compliance Checklist: Level 2 Timelines
The time required to meet CMMC Level 2 requirements varies depending on your organization’s size, industry, and whether or not you already comply with NIST 800-171 or a similar framework.
Below are timelines to show what an average organization can expect for CMMC Level 2.
**The following timeline assumes that the organization will start with a gap assessment and follow a typical implementation plan. Organizations that are already aligned with NIST 800-171 can proceed faster.
CMMC Level 2 Timeline (6-8 Months)
Gap Assessment and Planning (1-2 Months)
- Determine the type of CUI your organization handles
- Map data flows for CUI and list out the systems involved in processing it
- Conduct a gap assessment against the 110 controls
- Draft your POA&M and create an implementation roadmap
Control Implementation (3-4 Months)
- Implementation of 110 controls, including access control, endpoint protection, backup and disaster recovery, incident response, and change management policies.
Documentation and Internal Validation Prior to Audit (1 Month)
- Internal testing of controls
- Vulnerability scan and patching
- Finalize documentation of evidence
C3PAO Audit (1 Month)
- Pre-assessment (optional, but strongly recommended)
- Official audit with interviews, control verification, and documentation review
- Validation of compliance (ongoing)
**Note: A vCISO can streamline the process and fast-track you to audit readiness. Rhymetec works closely with trusted auditing partners and can connect you with them for your assessment.

Advantages of Engaging A CMMC Consultant (The Earlier, The Better!)
The higher levels of CMMC are complex.
If you aren’t already compliant with the relevant NIST frameworks, compliance for Level 2 will require implementing a massive amount of technical controls and corresponding documentation. For many companies, it simply doesn’t make sense to try to manage all of this internally.
This is where a virtual CISO (vCISO) comes in.
A vCISO works closely with your team to understand your environment and translates CMMC requirements into what you actually need to accomplish.
Our vCISOs at Rhymetec support you throughout the entire CMMC preparation process. We conduct your gap assessment, carry out control implementation for the controls you need, finalize documentation, and serve as the main contact point for auditors on your behalf.
**For information on our vCISO pricing options, check out our blog on vCISO pricing.
Outsourcing the bulk of the work required for CMMC is helpful at any point in the compliance process, but is especially transformative during the initial stages. In our experience, especially partnering with startups to meet their compliance goals, working with a vCISO from the beginning allows you to turn an onerous process into a business enabler.
An experienced vCISO will build a security program for your organization that not only meets CMMC and requirements but scales as your business grows. They understand exactly how to structure your compliance program to enable you to more easily meet additional or future requirements in your industry, and can connect you to the best auditing partners in your space.
Partner For Success: Work With Rhymetec + An Accredited C3PAO
Meeting CMMC requirements is a complex process.
The good news is that you don’t have to do it alone. Our partnership with industry leader A-LIGN, an accredited C3PAO, gives you access to both the security legwork needed to meet requirements as well as certified assessment services.
Together, we help organizations prepare for CMMC with confidence. Whether you are just getting started or finalizing your readiness for an assessment, we’re here to support your compliance journey with security expertise and a trusted C3PAO partner.
C3PAOs are the only organizations authorized by the CyberAB to perform official CMMC assessments. Their involvement is essentially a must-have for any contractor aiming for certification. Meanwhile, as a Registered Provider Organization (RPO), Rhymetec works hand-in-hand with A-LIGN to help you prepare for that assessment.
RPOs are approved to offer consulting and readiness support, and help you implement required controls, remediate gaps, and make sure your security practices and documentation align with CMMC standards. Together with A-LIGN, we are proud to offer this streamlined option for our clients. Contact us todayto learn more.
Over 80% of breaches involve weak or misused credentials, according to Verizon’s Data Breach Investigations Report. This is a clear example of just one risk that represents both a security and a compliance risk for organizations, as it impacts everything from the efficacy of your cybersecurity program to compliance audits, contracts, and revenue.
For federal contractors handling Federal Contract Information (FCI), CMMC Level 1 directly addresses this risk and other pressing ones. Level 1 is designed to encourage basic cyber hygiene, and outlines 15 controls that help safeguard sensitive data and maintain eligibility for federal contracts.
In this blog post, we will go over a CMMC Level 1 checklist and requirements, starting with which types of organizations Level 1 applies to:
Government contractors, subcontractors, and suppliers in the federal supply chain that handle FCI (Federal Contract Information) likely fall into CMMC Level 1. This tier is designed for contractors and subcontractors working with the Department of Defense who don't store or process sensitive technical data but still have access to basic contract details, for example.
CMMC Level 1 has 15 requirements. Your organization must meet these 15 requirements and self-attest against them each year. The requirements fall under basic safeguarding practices and are derived from the Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) 52.204-21.
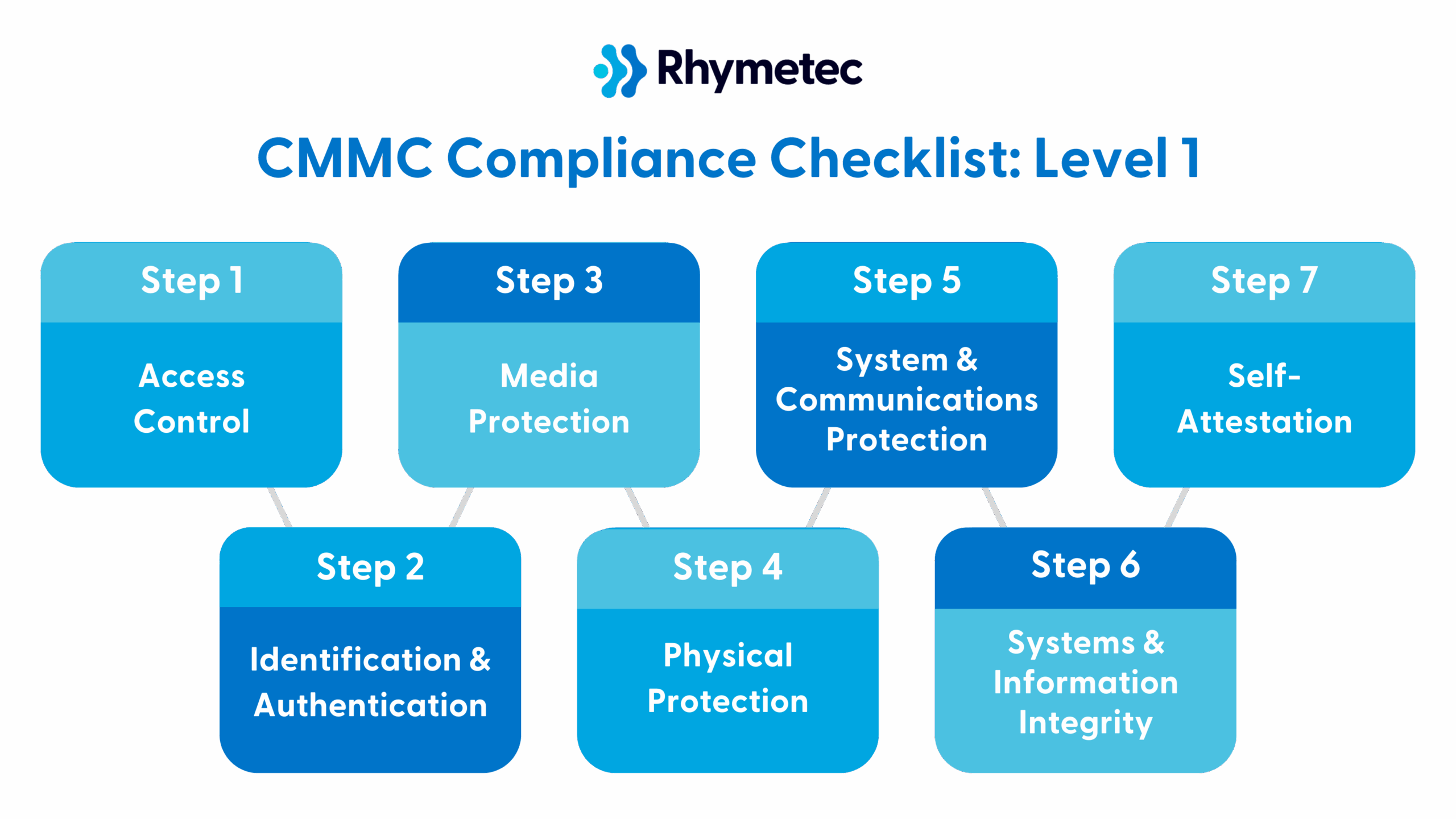
Below is our CMMC Level 1 Checklist, starting with the gap assessment process and then walking you through the 15 requirements that need to be addressed:
Getting Started - CMMC Level 1 Checklist: Gap Assessment
"At Rhymetec, we always start with a gap assessment. A gap assessment against the NIST 800-171 controls is a must-have…It helps you determine if you have any missing controls or if you have any gaps in your compliance, so you can start putting together a roadmap for completing the remaining controls." - Metin Kortak, Rhymetec
The aim is to compare your current environment against the required controls. This process tells you what needs to be done before you’re ready to self-attest or move into the certification phase.
CMMC 2.0 also allows you to use a Plan of Action and Milestones (POA&M) to formally track missing controls and your plan for implementing them:
“In 2.0, CMMC came out with a final action and milestones plan. This document essentially allows you to create implementation plans for controls that are missing in your gap assessment, so that you can remediate these controls within a certain amount of time. This is also something you can work with third parties on or conduct your own self-assessment.” - Metin Kortak, Rhymetec
Next, we'll break down what you need to do to meet the requirements of CMMC Level 1.
CMMC Level 1 Checklist
If your organization handles only FCI and not CUI, then CMMC Level 1 likely applies to you.
"If you're only handling FCI and not CUI, you fall into Level 1. Level 1 is an order of magnitude less involved than Level 2. It actually only has 15 requirements that are heavily aligned with a subset of the NIST 800-171 framework. You must meet these 15 requirements, and then you just need to self-attest against them each year." - Matt Bruggeman, A-LIGN
This tier is designed for contractors and subcontractors working with the Department of Defense who don't store or process sensitive technical data but still have access to basic contract details, for example. The 15 requirements fall under basic safeguarding practices and map to NIST 800-171, Rev. 2, specifically from Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) 52.204-21.
Below are the 15 action items you need to address for CMMC Level 1, divided into clear sections based on our expert advice.
*For a full list of these items with a greater level of technical detail, see the official FAR 52.204-21 documentation.
Access Control
1. Limit system access to authorized users.
To reduce the risk of unauthorized exposure of data, only users with a business need should be able to log in to systems that store or process FCI.
In practice, what you’ll need to do is action items such as setting up role-based access controls, implementing IAM (identity and access management) tools, and regularly auditing user access to remove accounts if they are no longer needed.
These types of security measures entail broader business benefits, as they reduce the risk of insider threats and limit the extent of potential damage in case of compromised credentials.
2. Limit system access to authorized devices.
Even if a user is not authorized, their device might be without the proper controls.
All laptops and mobile devices connected to your systems should be managed to prevent untrusted endpoints from introducing threats. Implementing Mobile Device Management or endpoint detection and response solutions are industry-standard methods to accomplish this and prevent threats from entering through untrusted endpoints.
3. Control access to system functions (e.g., user roles).
Users should only be able to perform actions appropriate for their job (such as admin tasks being restricted to IT staff). It is critical to define roles and assign permissions accordingly, and restrict admin rights to select personnel.
These measures vastly minimize the risk of unauthorized changes or even accidental misconfigurations being made.
4. Verify control connections to external systems.
Any systems that link with a third party (such as a cloud storage provider or file-sharing services) can become gateways for data leaks. As such, they must be reviewed and approved to prevent unauthorized data transfers.
Organizations can accomplish this by maintaining an inventory of all third-party connections, reviewing and approving integrations before use, and monitoring data flow between internal systems and external services. This serves to protect against data loss via insecure APIs or file-sharing platforms.
Identification and Authentication
5. Require user identification before granting system access.
Every action should be traceable to an individual.
Action items to accomplish this objective include assigning unique user IDs to all personnel, eliminating any shared accounts, and enabling logging to tie activity back to specific users.
The business value of this step is crucial, as it creates accountability and aids in forensic investigation in case of incidents.
Media Protection
6. Sanitize or destroy media containing FCI before disposal.
Leaving data on discarded devices is a common but extremely preventable risk.
Simply establishing a process to wipe drives using certified tools, physically destroy storage devices when decommissioned, and document sanitization or destruction (for audit purposes) accomplishes this and prevents data leakage from improperly discarded hardware.
7. Protect FCI stored on removable media and external drives.
Portable storage can create unique risks when used off-site, and it’s critical to protect data in the event devices are lost or stolen.
Avoiding the use of removable media altogether is the best way to circumvent this risk entirely, but if your organization has to use removable media, you should be encrypting USB drives and external hard drives and locking physical storage devices when not in use.
Physical Protection
8. Limit physical access to systems storing or processing FCI.
Unauthorized individuals shouldn’t be able to walk up to a server or terminal.
Acceptable measures to fulfill this requirement under CMMC Level 1 include using keycards, biometric access, or badge systems, monitoring entry points with surveillance, and keeping visitor logs. All of these measures greatly reduce the risk of physical tampering and/or data theft.
System and Communications Protection
9. Monitor and control communications at system boundaries.
Network traffic needs to be inspected and controlled to catch threats early.
Firewalls and intrusion detection tools are used to monitor traffic entering or leaving your network and block suspicious activity, and setting up logging and alerting for traffic anomalies cues you into threats early on.
10. Implement boundary protections such as firewalls and filters.
Network segmentation can both contain threats and reduce their impact.
Actions such as applying email filters and web proxies, enforcing traffic rule zones between zones, and creating VLANs to isolate sensitive systems will limit the radius of a breach and keep attackers from causing further harm.
11. Use cryptographic methods when transmitting FCI.
Sensitive data in transit needs to be protected from being intercepted. The recommended controls around this are enforcing TLS for all network communications, using secure transfer protocols, and encryption.

Systems and Information Integrity
12. Identify system flaws (e.g., patches) and manage them.
Outdated systems are prime targets for attackers. This is why it is crucially important to keep systems up to date by applying security patches regularly.
For CMMC Level 1, organizations need to be accomplishing this by prioritizing critical updates, applying patches on a schedule with a documented process, and regularly checking for software updates.
13. Take steps to protect against malicious code, such as antivirus.
Malware can compromise systems and exfiltrate data. To combat this risk, deploying anti-malware tools to block viruses and other threats that could compromise FCI are industry standard steps.
14. Monitor system activity for security events.
Without visibility, threats can go undetected for months. It’s crucial to set up a way to track system logs in order to detect unusual behavior that could indicate a breach or misuse. To accomplish this, organizations often implement a SIEM platform, or other tools to monitor for suspicious behavior.
15. Perform periodic system scans and take corrective action.
Running regular vulnerability scans to detect weaknesses and applying fixes or updates as needed to keep systems secure is something every organization should be doing. The business value of this last control is keeping your security posture strong and supporting audit readiness.
CMMC Level 1 Checklist: Self-Attestation For CMMC Level 1
Unlike Level 2 and Level 3, Level 1 does not require a third-party assessment.
Instead, your organization must annually self-attest to meet all 15 practices. That attestation must come from a senior company official and be submitted through the Supplier Performance Risk System (SPRS).
Most organizations will need to document the following for Level 1:
- How are these 15 controls above are implemented
- Which systems process or store FCI
- Who is responsible for each requirement
- Dates of the last review and updates
Although Level 1 is a massive degree less resource-intensive than Level 2 or 3, that doesn’t mean that accountability is any less important! Contractors who don’t meet these requirements can face contract risks.
Here is how long you can anticipate CMMC Level 1 to take:
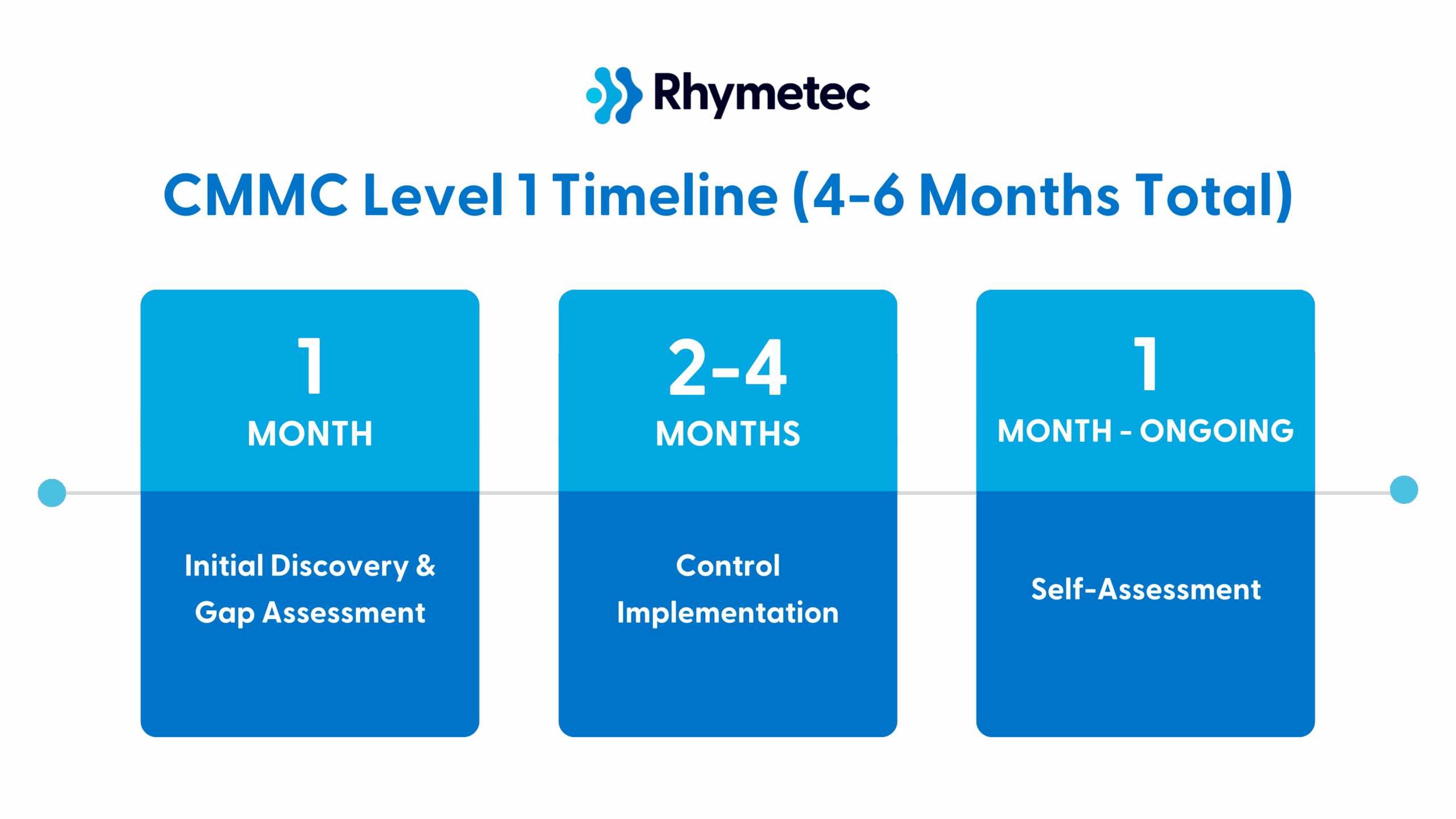
Partner For Success: Work With An Accredited C3PAO
Meeting CMMC requirements is a complex process, even for Level 1.
The good news is that you don’t have to do it alone. Our partnership with industry leader A-LIGN, an accredited C3PAO, gives you access to both the security legwork needed to meet requirements as well as certified assessment services. Working with trusted partners speeds up the timeline for CMMC.
Together, we help organizations prepare for CMMC with confidence. Whether you are just getting started or finalizing your readiness for an assessment, we’re here to support your compliance journey with security expertise and a trusted C3PAO partner.
C3PAOs are the only organizations authorized by the CyberAB to perform official CMMC assessments, if you need to go beyond self-assessments. Their involvement is essentially a must-have for any contractor aiming for certification. Meanwhile, as a Registered Provider Organization (RPO), Rhymetec works hand-in-hand with A-LIGN to help you prepare for that assessment.
RPOs are approved to offer consulting and readiness support, and help you implement required controls, remediate gaps, and make sure your security practices and documentation align with CMMC standards.
Together with A-LIGN, we are proud to offer this streamlined option for our clients. Contact us today to get started.
In 2025, more companies than ever before are budgeting for ISO 27001 certification costs. In a recent ISO survey, the global number of ISO 27001 certificates reached over 70,000 certificates and were reported in 150 countries and across a range of economic sectors.
Many of these certifications are driven by customer demand and procurement requirements, in particular in fields such as B2B SaaS.
Understandably, cost is often one of the most important questions companies exploring their compliance options have. ISO 27001 is a bit more involved than other frameworks in this space, such as SOC 2, as it requires a broader set of security controls and third-party requirements.
External audit costs, internal resource time, implementing technology changes at your organization, and ongoing maintenance all factor into ISO 27001 certification costs. Without a clear breakdown, it can be easy to underestimate both the initial investment and the ongoing effort.
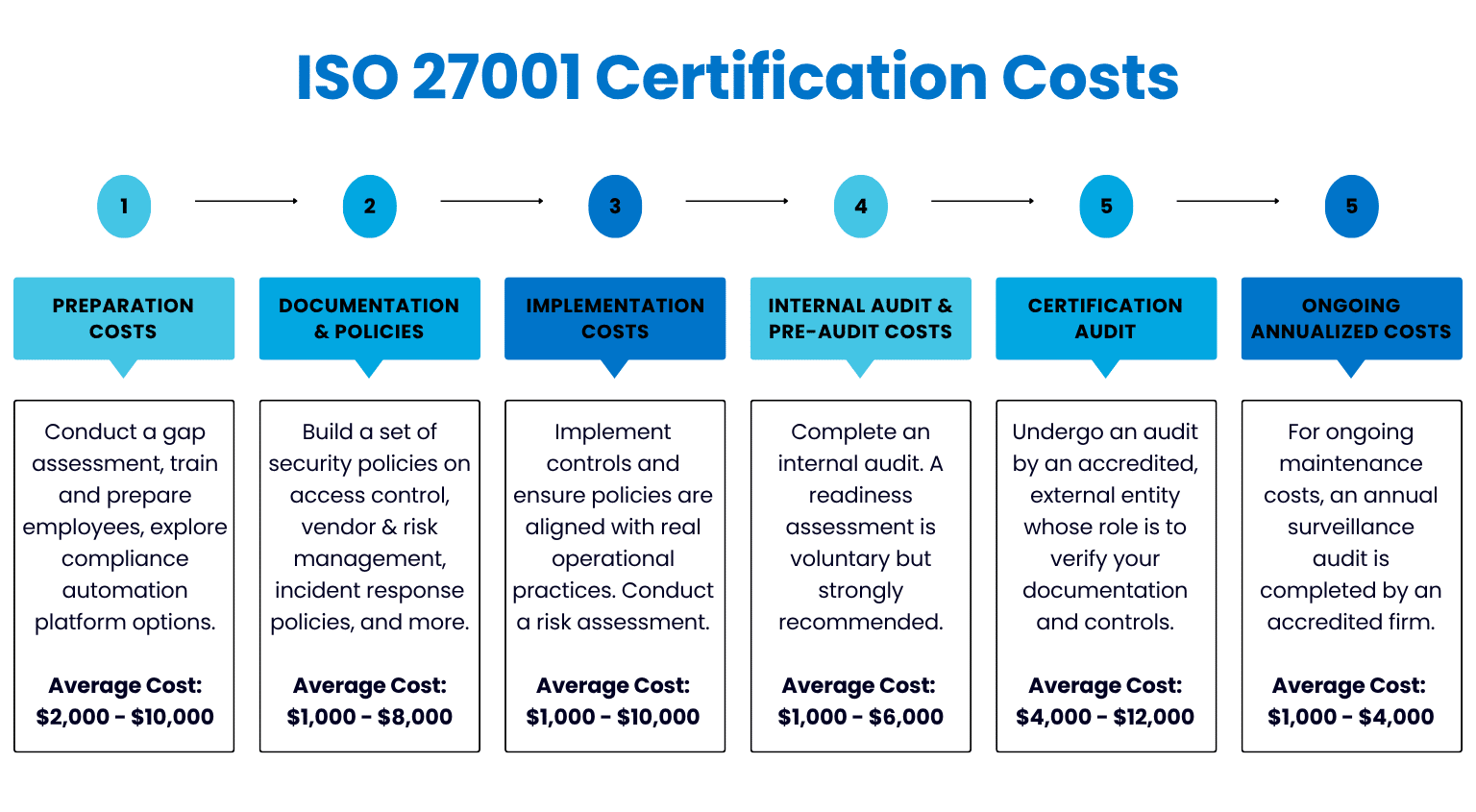
This blog outlines what to expect for ISO 27001 certification costs, based on current market data, our team’s firsthand experience working with SaaS startups, and input from certified auditors we work closely with.
Preparation Costs
Preparation costs for ISO 27001 represent a substantial part of the overall investment. Before engaging a registrar (an accredited certification body), your organization must complete a range of activities that require time, resources, investing in new technologies, and, in many cases, external support.
Typically, the first step of an ISO 27001 engagement is a gap assessment. A gap assessment shows where you are versus where you need to be by identifying missing controls and policy gaps in comparison to the ISO 27001 standard. Companies may complete this assessment internally or work with a third-party consultant for greater objectivity and expertise (if you don’t have in-house personnel with compliance experience).
Following the gap assessment, staff training and security awareness are typically the next steps.
Every employee needs to understand their role in protecting both company and customer data. Your organization will likely need to develop new onboarding materials, invest in employee training sessions, and plan targeted training sessions for engineers and leadership.
The adoption of new software for compliance is often included in the preparation phase. Startups in rapid phases of growth typically select to use tools like Drata or Vanta to automate the pieces of compliance that can be automated, and keep track of their progress in one central place.
These tools support policy management, control tracking, evidence collection, audit preparation, and more. These platforms can vastly simplify the compliance process, but they do entail an investment. Check out our blog post on compliance automation platforms for more information on how these tools work and how they accelerate compliance.
Each one of these preparation activities helps to create a foundation for a successful certification process. Companies that invest early on in assessments, training, and new technologies tend to move through the audit with greater efficiency and fewer surprises. While the cost ranges vary, the effort spent up front directly impacts how much time and work will be needed later on.
Estimated Total Cost of Preparation: $2,000 - $10,000
ISO 27001 Certification Cost: Documentation and Policy Development
ISO 27001 requires formal documentation of the Information Security Management System (ISMS), including your policies and procedures. Documents are reviewed during the audit and must align with how your organization operates in practice.
For this step, most companies begin by building out a core set of policies around access control, vendor management, risk management, acceptable use policies, incident response policies, and asset management. Policies must reflect actual practices and responsibilities that are implemented.
While templates can be used to accelerate this step, customization specific to your organization is important. This is a good example of where using a compliance automation tool (such as Vanta or Drata) in combination with working with an expert security and compliance professional (such as our vCISOs at Rhymetec) can be extremely helpful:
The compliance automation tool provides an excellent baseline, while a dedicated team can customize documentation and policy development to your organization in a way that will pass scrutiny during your audit.
Some companies choose to adopt a full ISMS documentation toolkit or policy automation platform. Although optional, these tools simplify everything from version control to auditor access and stakeholder review, but they do come with additional software costs.
Your documentation will be one of the most scrutinized aspects of your ISO 27001 audit. It’s critical to adequately plan out enough time and resources to draft, review, and align policies with actual practices. Building out your policies with day-to-day operations in mind can help streamline the audit process while supporting long-term security and compliance.
Estimated Cost of Documentation and Policy Development: $1,000 - $8,000
Implementation Costs: Building The Framework
Once documentation is drafted, the next step is to begin actually implementing the controls required by ISO 27001.
The most critical piece of this phase is making sure your policies are aligned with real operational practices. Additionally, at this stage, you will assign responsibilities and validate that controls work as they are meant to. Costs can also add up during the implementation phase from technology upgrades you may need.
Conducting a risk assessment and documenting a plan to mitigate any identified risks is also a key part of this stage. Many companies choose to circumvent the need to acquire new technologies and dedicate internal resources by engaging a vCISO (Virtual CISO). At Rhymetec, our vCISOs take the implementation work off your plate and accomplish these items for you.
Estimated Implementation Costs: $1,000 - $10,000

Internal Audit and Pre-Audit Expenses
Before undergoing your certification audit, you’ll need to complete an internal audit.
In many cases, organizations will outsource this step to a firm specializing in pre-audit assessments (or, if you are already working with a vCISO, they will do this work for you!). Organizations with internal teams can manage this on their own, but many choose to work with outside consultants to speed things up and ensure objectivity. It’s important to note that it’s encouraged to find internal auditors who are PECB-accredited.
The pre-audit, or readiness assessment, is a voluntary but highly recommended assessment typically carried out by a consultant (such as a vCISO) or the certification entity. This serves to mimic your official audit, identifying areas of weakness and reducing the risk of non-conformity during your real audit. Costs during this stage also reflect the need to revise any discovered gaps, finalize your evidence collection, and coordinate between teams.
Estimated Internal Audit & Pre-Audit Costs: $1,000 - $6,000
Certification Audit Costs
After you’ve completed your ISO 27001 readiness work, the ISO 27001 certification audit is conducted by an accredited, external entity. The process is divided into two phases:
Phase 1 - Verifies your documentation.
Phase 2 - Verifies that controls are working as intended.
Costs depend primarily on organizational size, which region you are in, how complex your infrastructure is, and the level of risk associated with your operations. The total cost of the audit covers both of these phases. For startups or for SMBs with less than 100 employees, the audit typically takes anywhere from a few days to two weeks.
If areas of non-conformity are discovered during the audit, it may be necessary to undergo a follow-up audit after making changes. This can cost extra as well. Some auditing firms also tack on administrative costs, in addition to the baseline cost of the audit.
Estimated Cost For Accredited ISO 27001 Audit: $4,000 - $12,000
Ongoing Costs: Maintaining Your Certification
Once certification has been obtained, your organization must maintain the ISMS and undergo annual surveillance audits. This requirement generates a recurring set of compliance activities to be completed every year:
The annual surveillance audit is completed by an accredited firm. While less demanding compared to the original audit, it’s still an obligatory step. Your internal team or vCISO will manage updating documentation, risk remediation where needed, technical control updates, and more.
Additionally, every three years your organization will need to undergo a recertification audit, with costs similar to the initial audit. This is built into the overall ISO 27001 certification costs for ongoing maintenance.
Estimated Ongoing Costs (Annualized): $1,000 - $4,000
Additional Factors That May Influence Your ISO 27001 Certification Cost
While most organizations follow a similar certification process, a number of variables can influence total cost. The following factors will affect the duration of your audit, internal preparation effort, and the level of external support needed:
Company Size and Structure
Larger teams, companies with multiple office locations, or hybrid work environments tend to increase both the number of controls and the audit scope. Costs due to these factors add up in terms of time spent on audit activities, documentation, and coordinating with internal teams.
Level of Technical Complexity
Companies with custom infrastructure, multi-cloud environments, or proprietary platforms often require additional effort in terms of documentation and control verification. Auditors also need to spend more time reviewing technical evidence in these cases.
Systems and Vendors That Are In-Scope
The number of systems and third-party services included in the ISMS directly affects the depth and length of your audit. Most companies include at least a dozen vendors in their initial ISO 27001 scope.
Internal Experience Level
Companies without prior compliance experience will require a greater level of external guidance. Meanwhile, teams that are already familiar with SOC 2 or similar frameworks tend to move faster and are able to reduce external costs.
The controls required for ISO 27001 overlap with several other popular frameworks in this space. If you already have SOC 2, for example, your organization can leverage some of those requirements to meet some of the ISO 27001 requirements.
Auditing Body Selection
Certification bodies charge different rates and employ slightly different methodologies. Regional pricing differences, travel costs, and preferred audit partners can influence the final quote.
Total ISO 27001 Certification Cost
For most startups and SMBs, the full cost of ISO 27001 certification falls between $10,000 - $50,000. This covers everything from preparation, implementation, internal and external readiness assessments, the official audit, and the first year of ongoing expenses.
Companies building from scratch and managing the process on their own will fall toward the higher range, while companies that opt to engage external support (such as a vCISO) will see lower overall bundled costs, even if they are starting from scratch.
This cost is front-loaded in year one, with most of the budget being allocated before and during the initial audit. After certification, annual maintenance costs are typically much lower.
In Conclusion: Planning For ISO 27001 Certification Cost
ISO 27001 certification is a multi-phase effort that touches nearly every part of a company’s operations. The audit itself is just one part of the full cost. Preparation work, implementation of the ISMS, internal (and external) testing, and ongoing maintenance all contribute to the total budget.
Companies that plan early on and understand their internal capacity are better positioned to keep costs under control. For early-stage teams, the main drivers of cost are scope, control maturity, and whether you’re handling the work internally or bringing in outside help.
Most startups and small to mid-sized companies spend between $10,000 - $50,000, depending on how much needs to be built from scratch. Large corporations may spend over $100,000, depending on their industry and the complexity of their operations. At Rhymetec, our vCISO pricing depends on which tier of support you select:

Properly budgeting for ISO 27001 certification costs enables organizations to get certified while building sustainable security practices that scale as the business grows. Whether you are in the early stages of building your compliance program or if you have already started the work and feel stuck, our experts can assist. Contact us today to get started.
The federal government spends more than $100 billion annually on IT services, much of it through contracts with private companies. That level of investment brings strict cybersecurity expectations, especially for contractors that handle government data.
Two frameworks frequently encountered in this space are the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) and the Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP). Both programs share the same goal of protecting sensitive information. However, they serve slightly different purposes and apply to different types of vendors.
CMMC is designed for companies working with the Department of Defense, in particular for those that handle Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI). Over 100,000 companies are part of the Defense Industrial Base. Any of them that handle CUI will eventually need to meet CMMC Level 2 or 3.
Meanwhile, FedRAMP applies to cloud service providers working with civilian federal agencies. If you are a defense contractor, a SaaS provider, or if your organization supports both civilian and DoD programs, it's important to understand how CMMC and FedRAMP compare.
This article outlines the main differences between CMMC and FedRAMP, including which types of organizations they apply to, the requirements of each framework, and how to handle certification.

Who Needs CMMC and Who Needs FedRAMP?
CMMC and FedRAMP apply to different groups of contractors and vendors based on two factors:
- The agencies they serve, and
- The type of data they handle.
In short, if you're in the DoD supply chain, you may need to meet CMMC. If you're a cloud provider for civilian agencies, you may need FedRAMP authorization. Some organizations may need to pursue both if they serve both sides of the government in these capacities.
Below is a non-exhaustive list of a few common types of companies to which CMMC would apply. Remember that CMMC applies to companies that do business with the Department of Defense (DoD) and process, store, or transmit Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) or Federal Contract Information (FCI):
- Defense manufacturers that produce components for aircrafts, vehicles, or weapons systems.
- Managed IT providers that support DoD facilities or systems.
- Staffing firms placing personnel in DoD programs (that involve access to CUI).
- R&D firms involved in any military-related developments or prototypes under DoD contracts.
- SaaS companies providing support to DoD missions.
- …and more.
Basically, if a company touches DoD contract information in any way (and in particular if it involves CUI), it will most likely fall under CMMC.
FedRAMP, on the other hand, applies to cloud service providers that want to sell their platforms or applications to civilian federal agencies (non-DoD). The types of companies this would include are:
- SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS vendors offering cloud-based products to agencies like the Department of Energy, the Department of the Treasury, or the Environmental Protection Agency.
- Data analytics platforms with cloud infrastructure that hosts government data.
- Project management or HR platforms that are seeking to be used across multiple federal departments.
- File storage, communications, or productivity tools that may process or store government records.
- Software vendors selling through government marketplaces like FedRAMP.gov or GSA Advantage.
For more information on what you will need to plan for to meet CMMC requirements specifically - and depending on which level of CMMC you need - check out our CMMC Level 1 Checklist and our CMMC Level 2 Checklist.
Security Requirements Compared
While CMMC and FedRAMP indeed share some overlap given their common goal to protect sensitive government data, they are built on different baseline requirements, and their approaches to security controls differ.
CMMC is based on the NIST SP 800-171 framework. It requires organizations to implement 110 security controls across 14 control families if they handle CUI and need to meet Level 2 certification. For organizations handling only FCI (Federal Contract Information), Level 1 requires 15 controls focused on basic security hygiene. CMMC's overall requirements are structured around the following security considerations:
- Access control
- Incident response
- Configuration management
- Personnel and physical security
- System and communications protection (measures such as encryption and traffic monitoring).
Additionally, organizations must also produce documentation, including System Security Plans (SSPs) and Plans of Action and Milestones (POA&Ms), and be ready for assessment by a third-party assessment organization (C3PAO) at Level 2 or 3. Lastly, it's important to note that CMMC 2.0 is not a point-in-time audit. Contractors are required to maintain compliance continuously. For Levels 2 and 3, assessment will lapse upon failure to annually affirm, according to the DoD's CMMC Guidance.

FedRAMP, by contrast, is based largely on NIST SP 800-53 controls, which are a bit more complex in scope. A Moderate FedRAMP authorization requires over 300 controls across a wide range of domains, including:
- Continuous monitoring of systems and data.
- Incident response procedures and breach notification timelines.
- Risk assessment processes and security authorization packages.
- Documentation of how systems are interconnected/dependent on each other.
- Penetration testing and vulnerability scanning.
- Independent third-party assessments.
FedRAMP places more emphasis on supply chain risk management, cloud architecture documentation, and the remediation of vulnerabilities. Cloud service providers must show that they have a set of documents to pass the Joint Authorization Board or agency review.
Documentation and Assessment Differences To Be Aware Of: CMMC vs. FedRAMP
The goal of documentation for CMMC (at Level 2) is to show that your organization meets the 110 controls from NIST SP 800-171. This includes documentation of:
- How controls are being implemented, and the plan for how they will be maintained. This documentation is your System Security Plan (SSP).
- A Plan of Action and Milestones (POA&M) - A list of gaps and a plan for remediation, with specific steps.
- A list of policies and procedures, showing how your organization covers access control, incident response, configuration management, and other security controls.
- Evidence of implementation (such as user logs, training records, configuration screenshots, etc) also must be included in your documentation.
Finally, assessment is conducted by a C3PAO (Certified Third-Party Assessment Organization) for Level 2. Self-assessment is allowed at Level 1 (and in some cases, for Level 2), but must still be documented in SPRS (Supplier Performance Risk System) and affirmed by a senior official.
*It's important to note that if you need CMMC Level 3, you will still need C3PAO affirmation completed on an annual basis, according to the DoD's updated overview of CMMC. For CMMC Level 3, the ongoing C3PAO assessments are in addition to undergoing an assessment every 3 years by the Defense Contract Management Agency's Defense Industrial Base Cybersecurity Assessment Center (DIBCAC).
FedRAMP documentation, meanwhile, is part of a full authorization package submitted to either a sponsoring agency or the Joint Authorization Board. Required documents include:
- System Security Plan (SSP) - this can often reach over 600 pages for Moderate-level systems!
- A Privacy Impact Assessment that identifies how personal data is being collected, used, and protected.
- A Continuous Monitoring Plan detailing how your organization will monitor system changes, incidents, and vulnerabilities.
- An Incident Response Plan, showing how incidents will be reported and handled.
- Documentation showing how system changes are approved and tracked (also known as a Configuration Management Plan).
Assessment is carried out by a third-party assessment organization that has been recognized by the FedRAMP PMO (Program Management Office). FedRAMP requires ongoing authorization maintenance, which takes the form of monthly vulnerability scans, incident reporting, and annual reassessments.
How Certification Works: CMMC vs. FedRAMP
CMMC 2.0 certification is tied to a company's eligibility for Department of Defense contracts. Depending on the sensitivity of the data involved, contractors must meet either Level 1 (self-assessed) Level 2 (typically third-party assessed) requirements, or Level 3 (third-party assessed). As discussed in greater detail in the previous sections, the process entails the following steps:
The first step is to conduct an internal NIST 800-171 gap assessment to compare where you are versus where you need to be. The next step is to document your System Security Plan and Plan of Action and Milestones, followed by finally engaging a certified third-party assessment organization (for Level 2 and 3).

There is no central approval body, and certification is granted per contract, with the assessment scope being based on the environment that contains CUI.
FedRAMP follows a centralized authorization process managed by the FedRAMP Program Management Office. There are two paths:
- Agency Authorization. For this option, a single agency sponsors the cloud service provider and reviews the authorization package.
- Joint Authorization Board. Authorization via a Joint Authorization Board (which comprises the DHS, GSA, and the DoD) involves a higher bar of scrutiny.
For the FedRAMP process, your organization will work with a Third-Party Assessment Organization to complete your Security Assessment Plan and Security Assessment Report. You'll then need to submit a full authorization package through FedRAMP's secure repository, and finally, undergo ongoing monitoring after approval.
Can You Be Compliant With Both?
The short answer is yes.
If your organization provides cloud-based services to civilian agencies and works with the Department of Defense, you likely need to comply with both FedRAMP and CMMC. For example, a SaaS company that supports DoD contracts involving CUI will need CMMC Level 2, and if the same product is then sold to a civilian agency (like the Department of Energy), they will also need FedRAMP authorization.
CMMC and FedRAMP share foundational requirements from NIST standards. But it's not a direct map on - meeting FedRAMP Moderate, for instance, doesn't automatically mean you meet CMMC Level 2. The good news is it absolutely does reduce duplication in areas such as access control, system monitoring, and incident response.
If you do need both CMMC and FedRAMP, figuring out early on how to align both compliance efforts can reduce cost and headaches down the road. This is a common use case for working with a consultant to manage both tracks. A consultant has the experience implementing these requirements across a large spectrum of different types of organizations, and can help ensure efficient implementation.
When To Bring In A Consultant Or MSSP
A recent report by the U.S. Government Accountability Office shows that many small businesses in the defense industry lack the internal resources to implement NIST 800-171 without outside help. This illustrates a growing need for CMMC consultants and MSSPs.
In the report, many smaller businesses in particular expressed concerns about the costs and resources required for CMMC implementation. This is where outsourcing the process can be transformative. Outsourcing is a fraction of the investment that building out an in-house team to carry out the implementation process would be.
The fact is that organizations often wait too long to bring in help, and this can lead to missed deadlines and unnecessary rework. If you're pursuing CMMC, FedRAMP, or both, bringing in a consultant early can reduce risk and cost.
It can be a good idea to bring in a consultant or MSSP if you don't have internal staff with experience in NIST 800-171 or 800-53 implementation, if you're unsure how to scope your CUI, if you're being asked to respond to a security questionnaire and aren't confident in your answers, or if you need to align your environment for both frameworks.
A consultant will perform a gap analysis, build a compliance roadmap, draft documentation for you, implement technical controls, and fully prepare your team for assessment. For small and mid-sized organizations, especially those with aggressive go-to-market timelines, outsourcing to a qualified team helps avoid delays and prevents compliance from blocking growth.
About Rhymetec
Our mission is to make cutting-edge cybersecurity available to SaaS companies and startups. We’ve worked with hundreds of companies to provide practical security solutions tailored to their needs, enabling them to be secure and compliant while balancing security with budget. We enable our clients to outsource the complexity of security and focus on what really matters – their business. Contact us today to get started.
So, you're considering SOC 2 or ISO 27001 for the first time - and realizing just how much time and expertise it takes to actually get there. That's where Vanta (and Rhymetec!) comes in:
Vanta automates 90% of compliance monitoring through integrations with 300+ systems, real-time control insights, and automated evidence collection—enhancing your visibility into your security posture. Rhymetec handles the hands-on readiness tasks for you. The combination of Vanta with our tailored services delivers a faster, more manageable path to audit success.
Our team of experts at Rhymetec, by leveraging Vanta for you, accelerates every step of your compliance journey from the initial scoping phase to auditor handoff. We've helped over 1,000 organizations efficiently meet their security and compliance goals with this method. Here's how Vanta works in conjunction with our services, and how the platform can benefit you immediately, especially if you are early on in the process of compliance:
Vanta Automates Compliance Workflows
Vanta automates the visibility into tasks required to build a compliance program. One of the main value adds of Vanta is that it will handle the repetitive work for you and give you back your time to focus on what really matters - growing your business. Here's how it works, particularly for organizations early in their compliance journey:
Using Vanta circumvents the need to even get started on tedious manual spreadsheets and checklists. Instead, Vanta enables organizations to jump right in and leverage its capabilities, including system integrations and automated collection of evidence.
For instance, a startup pursuing SOC 2 may need to prove that it restricts employee access to production systems, monitors for security incidents, and keeps its asset inventory up-to-date and in line with SOC 2 requirements. Vanta connects to systems including AWS, GitHub, Google Workspace, and Okta to automatically accomplish the following:
- Display passing controls.
- Simplify policy management.
- Collect the evidence needed for an audit.
It also includes pre-built policy templates for every framework, so teams can work from a baseline and avoid having to write everything from scratch. Leadership is able to track compliance status in real time and improve visibility tied to audit preparation for employees—resulting in efficiency and reduced time to compliance.
Who Uses Vanta And Why
Vanta is primarily used by fast-growing, cloud-native organizations that are seeking to meet relevant security and data privacy requirements in the most efficient way possible. Often, these organizations are trying to avoid dedicating excessive internal resources to manual compliance work. However, we’ve seen companies from all sizes—startup to enterprise—with varying environments—such as multi-cloud and hybrid—utilize Vanta to streamline their compliance efforts.
Some of the main reasons companies opt to use Vanta are to help them:
- Reduce their audit timelines.
- Improve visibility into their security posture.
- Lower the overall cost of compliance.
Vanta connects to the tools you use via API, the cloud infrastructure you're set up in, and your internal systems to give you a complete view of your security and compliance.
This eliminates the need for fragmented spreadsheets and manual checklists, providing leadership more control over compliance progress and unburdening technical teams that are already stretched thin.
Another core value add is that Vanta enables a single source of truth for audit readiness, helping leaders and your sales team demonstrate you're where you need to be in terms of security and compliance to auditors, customers, your partners, and other stakeholders.
What Does Vanta Do? Vanta Supports Continuous Compliance
It's important to know going into your compliance journey that compliance doesn’t stop after one audit.
Frameworks like SOC 2, ISO 27001, and HIPAA require ongoing evidence of control effectiveness, which means you need continuous monitoring rather than only point-in-time documentation.
Vanta is built precisely to support this model. It runs in the background, constantly monitoring your infrastructure and systems for changes that could impact compliance. It will flag any issues in real time, such as expired access, unapproved software, or missing security training. The platform centralizes the evidence you'll need to show controls are operating continuously.
This approach replaces manual check-ins and periodic reviews with continuous visibility. Combined with Rhymetec's guidance and remediation support, clients stay audit-ready year-round without having to rebuild compliance work from scratch each cycle.
Vanta Streamlines The Work of Cybersecurity & Compliance Experts
Vanta automates the visibility into tasks (While Rhymetec can support the completion of them) that are most likely to slow down compliance teams, allowing the experts to focus on higher-impact and more specific work. Tasks like collecting screenshots, tracking evidence, and managing spreadsheets shift to automated processes within the platform.
For Rhymetec's team, the platform provides a centralized source of truth and allows us to spend more time analyzing results and guiding clients through control implementation. Our team uses Vanta in every step of the compliance automation process on your behalf. By handling repetitive tasks and bringing issues to our attention automatically, Vanta allows us to carry out a more efficient process to compliance readiness for your organization.
How Rhymetec Leverages Vanta To Deliver Compliance - Fast
Rhymetec leverages Vanta as a core part of our compliance delivery model.
Our approach combines all of the benefits of automation with hands-on cybersecurity expertise to shorten the path to audit readiness. Our team configures Vanta for your systems and selected framework. We work hard to eliminate common setup delays and create alignment between compliance goals and actual business operations.
Once deployed, Vanta automatically monitors your cloud infrastructure and systems for compliance-related activities. But automation alone doesn’t get you audit-ready. That’s where Rhymetec comes in. After the initial setup, our team steps in to:
- Interpret and prioritize Vanta’s findings based on your unique business needs
- Remediate flagged issues with hands-on support — not just advice
- Tackle all remaining manual components like policy creation, access reviews, evidence collection, and control implementation
The combination of automated and manual work keeps the momentum going and gets clients through readiness assessments and audits on a much faster timeframe. By managing both Vanta and the 'hands-on' components of compliance readiness work on your behalf, we’re able to accelerate every phase of the compliance process.
Why Pairing Vanta and Rhymetec Delivers Better Outcomes
Most frameworks require an array of expert judgment, manual implementation of certain controls, and a level of preparation that automation can't complete 100% of on its own.
Rhymetec fills that gap by managing the manual work and aligning Vanta specifically to your environment. We interpret control requirements, resolve flagged issues, write custom policies, manage communication with auditors on your behalf, and more.
By using Vanta for compliance automation - and Rhymetec filling in the gaps for you when needed - clients move faster and meet their compliance goals with less internal burden. Together, we consistently generate strong audit readiness and stronger security programs.
Accessing Vanta Through Rhymetec
Rhymetec is proud to offer Vanta (in conjunction with our Vanta compliance services) directly to clients who haven't yet selected a compliance automation platform.
Particularly in the case of clients early in their compliance journey, this vastly simplifies the buying process by providing both the technology and the services needed to meet requirements in one engagement. We give clients access to a world-class platform without requiring them to manage separate vendor relationships or navigate pricing and setup alone.
Our team at Rhymetec handles everything from the initial deployment and setup in Vanta to ongoing administration of the platform on your behalf. This allows you to adopt automation earlier, which will accelerate your compliance timelines and help you avoid missteps that a self-directed rollout could entail. Contact our team to learn more:
Deepak Chopra once said, "All great changes are preceded by chaos." This has never been more accurate than when it’s applied to the current AI and cybersecurity environments—and the regulations that govern them.
New frameworks like the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA), the EU AI Act, the Network and Information Systems Directive 2 (NIS2) and the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) are reshaping how businesses handle security, risk and compliance. These regulations aren't just about ticking boxes—they carry major financial penalties and demand real operational changes.
For companies in financial services, AI development, critical infrastructure or defense, staying ahead of the changes is vital to avoid penalties, protect data and maintain trust. Let's look at what each entails.
DORA: Protecting Financial Institutions From Cyber Disruptions
Financial institutions face constant cyber threats and operational risks. DORA aims to empower financial organizations to weather system disruptions and continue operating smoothly.
DORA requires penetration testing, vulnerability assessments and disaster recovery planning. It focuses on business continuity to ensure that if a system fails, a plan is in place to keep operations running. Banks, insurance companies and investment firms must validate security controls through rigorous testing.
This regulation is a wake-up call for financial institutions to take cybersecurity resilience seriously. The penalties for non-compliance are severe, making it crucial for businesses to invest in robust security testing and operational risk management.
The EU AI Act: Setting The Global Standard For AI Compliance
AI development currently operates in a regulatory gray area, but the EU AI Act is changing that. One of the first laws to set clear boundaries on AI usage, it focuses on ethical risks, security concerns and prohibited applications.
The most important takeaway is the significant financial penalties for non-compliance: These can be up to 7% of a company's global annual revenue or 35 million euros, whichever is higher. That's more than GDPR, which has already forced businesses worldwide to rethink their approach to data privacy.
This law explicitly bans certain AI applications, particularly those that exploit vulnerabilities. The ban includes AI-powered cyberattacks, social manipulation and unethical facial recognition practices. Article 5 of the act outlines prohibited AI uses, such as systems that exploit people's age, disabilities or socioeconomic circumstances.
This isn't simply a privacy factor; its purpose is to prevent AI from being weaponized.
A common misconception is that this law only affects European companies. That's not the case. Any company developing, deploying or processing AI systems in the EU—or serving EU customers—must comply. For example, if a U.S. company hosts its platform in an EU data center or processes European customer data, this regulation applies.
The EU AI Act is setting the stage for global AI governance. Similar regulations are expected to emerge worldwide, making it smart for businesses to adapt now rather than scrambling to comply later.
NIS2: Strengthening Cybersecurity For Critical Infrastructure
Also in the EU, the NIS2 Directive expands cybersecurity requirements for critical industries like energy, healthcare, transportation and digital services. It builds on the original NIS Directive but goes much further, applying to more organizations, increasing security expectations and enforcing stricter penalties.
The enhanced reporting requirements are one of the biggest challenges. Companies must notify regulators of cyber incidents within 24 hours, provide a complete assessment within 72 hours and demonstrate they are actively managing security risks.
The directive also emphasizes stronger supply chain security, holding companies responsible for ensuring their vendors meet cybersecurity standards. This means businesses can't just secure their own systems—they must also vet suppliers and partners to prevent weak links in the supply chain.
Beyond reporting and supply chain oversight, NIS2 enforces stricter governance requirements. Organizations must appoint security officers, conduct regular risk assessments and develop robust cybersecurity policies. Those that fail to comply face heavy financial penalties and increased regulatory scrutiny.
Compliance isn't optional for companies operating in or serving the EU market. NIS2 is setting a new cybersecurity standard, and businesses that don't act risk fines, operational disruptions and reputational damage.
CMMC: Raising the Bar For U.S. Defense Contractors
The CMMC is a requirement for companies working with the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD). It builds on cybersecurity frameworks like NIST 800-171, ensuring that defense contractors follow strict security protocols to protect sensitive government data.
Recent changes to CMMC include a new self-assessment option for Level 1 compliance, making it easier for smaller contractors to meet requirements without hiring third-party auditors. However, higher certification levels still require independent verification, adding layers of accountability.
With the new compliance requirements going into effect in mid-2025, businesses need to act now. The DoD has made it clear that CMMC certification will be mandatory for contracts, and companies that don't comply risk losing business.
Evolving Security Frameworks: A Smarter Approach To Compliance
For organizations handling sensitive data in healthcare, finance and other regulated industries, new security frameworks present a way to prove compliance with strict privacy and cybersecurity standards. In the past, certification required a lengthy, one-size-fits-all assessment, but newer models offer more flexible options with fewer controls, reducing complexity while maintaining security.
Many businesses don't realize that certification levels vary, and choosing a lower-tier option may not meet regulatory or customer expectations. This is especially important for HIPAA compliance, where recognized certifications can demonstrate that companies meet security standards. As cybersecurity laws evolve, understanding these frameworks ensures that businesses stay compliant, competitive and prepared for future regulations.
Laws like DORA, the EU AI Act and NIS2 are designed to keep technology from becoming a threat. AI development currently lacks clear rules—without oversight, it can be used in dangerous ways. These regulations force businesses to prioritize security and ethics upfront, preventing bigger problems down the road.
To stay ahead, organizations must:
- Identify relevant regulations and update security policies.
- Invest in risk assessments, penetration testing and employee training.
- Stay informed—more regulations are coming.
Compliance isn't just about avoiding penalties but about building a safer, more resilient digital future. Companies that act now will lead, while those that wait will fall behind.
You can read the original article posted in Forbes by Rhymetec CISO, Metin Kortak.
About Rhymetec
Our mission is to make cutting-edge cybersecurity available to SaaS companies and startups. We've worked with hundreds of companies to provide practical security solutions tailored to their needs, enabling them to be secure and compliant while balancing security with budget. We enable our clients to outsource the complexity of security and focus on what really matters – their business. Contact us today to get started.
Working with a CMMC consultant is an attractive option for many organizations seeking to meet the updated CMMC requirements nowadays.
The Department of Defense (DoD) released CMMC 2.0 on October 15th, 2024, a requirement for defense contractors and subcontractors with the goal of improving cybersecurity standards. The updated version refines the original framework, aiming to simplify the path to compliance while maintaining the highest security standards for organizations that handle Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) and other sensitive contract data.
One way in which the updated version simplifies compliance is by aligning requirements even more closely with existing cybersecurity standards like NIST SP 800—171. Many organizations may already comply with NIST 800-171 or another framework very closely aligned with it. Either way, the shift in compliance expectations has led many organizations to assess whether they have the in-house resources to manage security or if they need external support through a CMMC consultant.
Working with a Managed Security Services Provider that offers CMMC consulting services (like Rhymetec!) can help contractors meet CMMC 2.0 requirements efficiently. MSSPs take the work off your plate and help you meet your goals in the fastest time frame possible. We've helped over 1,000 organizations meet their compliance and security requirements in the fastest time frame possible.
In this article, we go over how CMMC 2.0 works, the options available for achieving compliance, and the potential advantages of working with a CMMC consultant.
What Is A CMMC Consultant, and What Do They Do?
Unless you have a fully built-out in-house cybersecurity and compliance team, CMMC can be a massive project to take on internally—taking a year or longer to meet requirements. This is where a CMMC consultant comes in.
A CMMC consultant is a cybersecurity and compliance expert who helps defense contractors meet the requirements of the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) 2.0. Consultants do everything from conducting a gap assessment to see where you are versus where you need to be, developing practical strategies to achieve compliance that will fit seamlessly (and as non-disruptively as possible!) into your operations, and guiding you through the certification process in partnership with an external auditor.
For many businesses, especially small and mid-sized contractors, understanding and implementing CMMC controls can be challenging. A CMMC consultant provides tailored, specialized knowledge to streamline the entire process, reduce your risk of non-compliance, and make big improvements to your overall security if you do not already have certain measures in place.
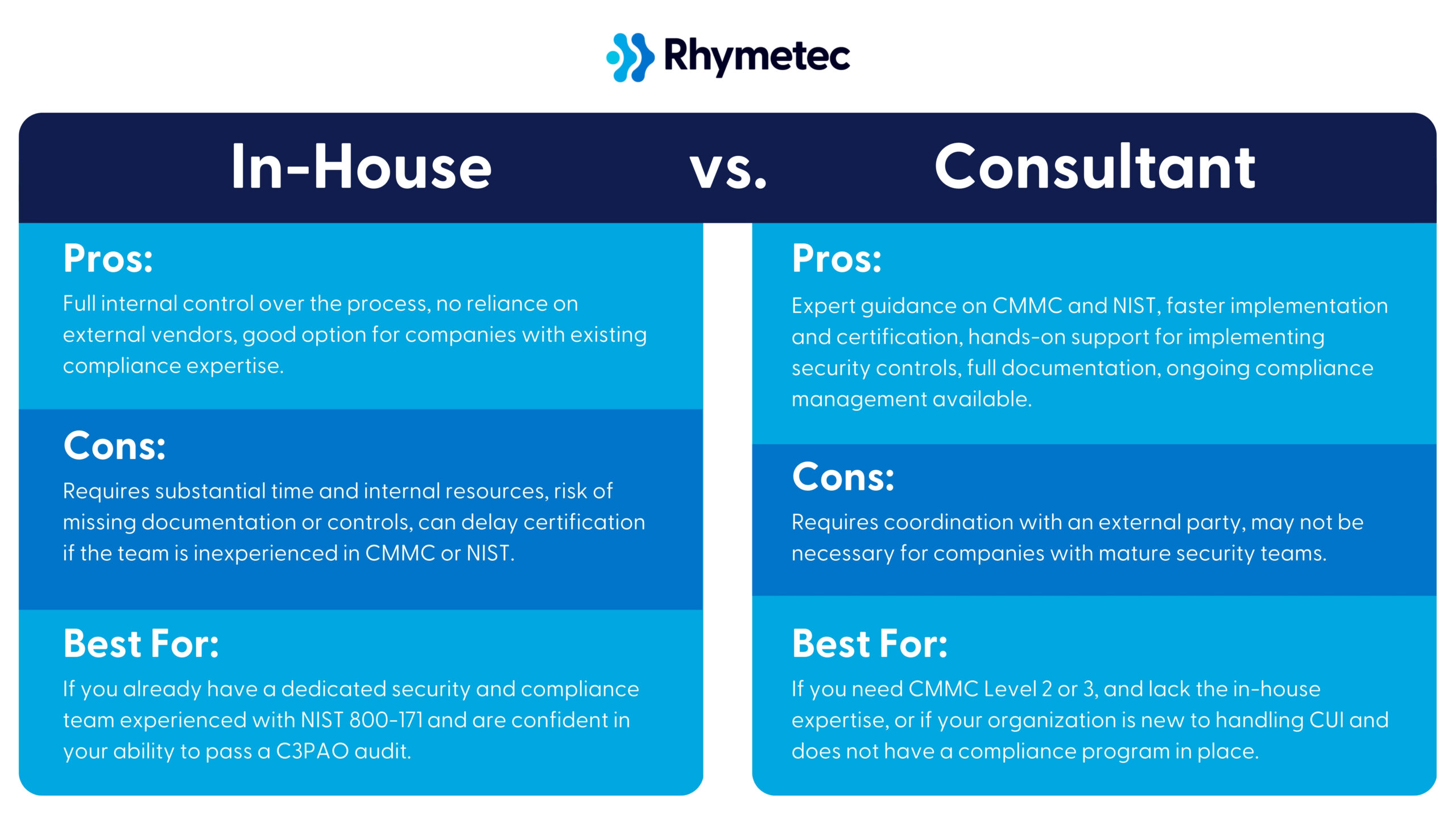
Do You Need A CMMC Consultant?
The best way to determine if you need a CMMC consultant is to look through the responsibilities and deliverables in the next section and assess whether or not you have the in-house capacity to fulfill all of these items.
If you are a larger organization and already have a security team with personnel that can accomplish the necessary tasks for CMMC (A Chief Information Security Officer, Penetration Tester, Cloud Security Specialist, Vulnerability Management Analyst, etc.), you can probably do most of this on your own or with guidance from a CMMC consultant rather than full support.
However, for smaller organizations or those without a fully developed in-house security program, engaging a CMMC consultant entails multiple benefits.
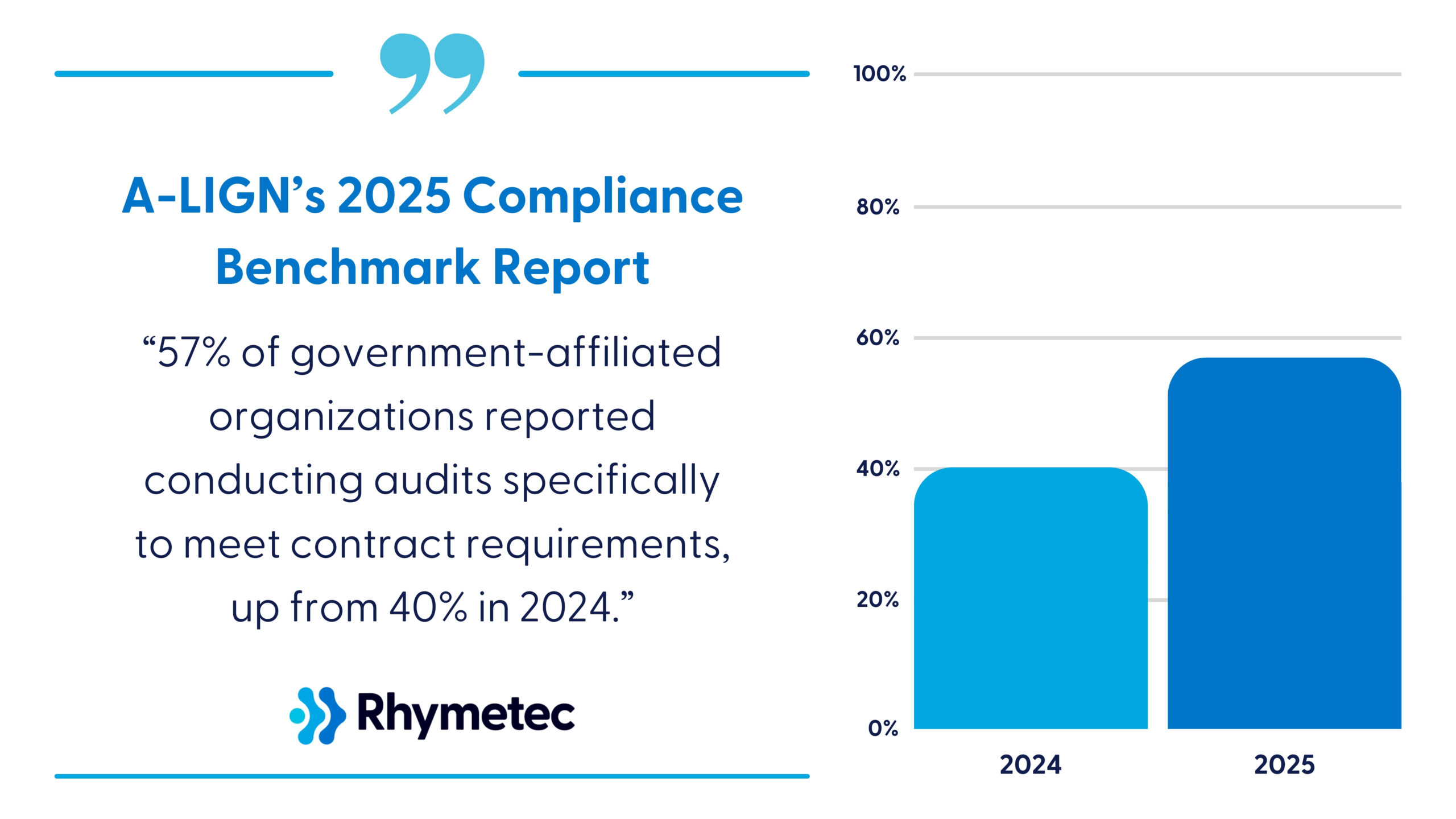
According to A-LIGN’s 2025 Compliance Benchmark Report, 57% of government-affiliated organizations reported conducting audits specifically to meet contract requirements, up from 40% in 2024. DoD contractors and subcontractors will need to obtain certification under one of three trust levels to demonstrate that they have adequately implemented cybersecurity measures.
Below are some questions to help you assess whether working with a consultant is the right choice. After you answer these questions and review the responsibilities and deliverables listed below in the next section, you should have a clear picture of whether or not you need a CMMC consultant:
1. Which CMMC Level Do You Need To Achieve?
The CMMC level you need depends on the type of contracts you handle:
CMMC Level 1 (Basic Cyber Hygiene) is required for contractors who only handle Federal Contract Information (FCI). Compliance is self-assessed, but security controls must still be implemented.
CMMC Level 2 (Advanced Cyber Hygiene) is required for contractors who handle Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI). Compliance requires a third-party assessment (C3PAO) every year.
CMMC Level 3 (Expert) is required for contractors who are working on high-security DoD projects. Compliance entails DoD-led audits and adherence to NIST SP 800-171 and portions of NIST SP 800-172.
If you need CMMC Level 2 or Level 3, working with a CMMC consultant can be extremely helpful, given the amount of work involved in the third-party assessment process, implementing missing security controls, and maintaining ongoing compliance.
2. Do You Have An Internal Cybersecurity Team With Compliance Expertise?
If you have a dedicated cybersecurity and compliance team, you may be able to handle CMMC requirements internally. Even if you do have an internal team, however, a CMMC consultant can still be beneficial if:
- Your internal team is unfamiliar with NIST 800-171 and CMMC requirements.
- You need help preparing evidence for a third-party assessment.
- Your security team does not specialize in compliance or lacks the expertise to develop CMMC procedures and policies.
3. Have You Implemented a NIST 800-171 Self-Assessment?
If you need CMMC Level 2 or Level 3, you should already have a NIST 800-171 self-assessment and an SPRS score recorded. If you haven't completed this step, a CMMC consultant can guide you through the process. Additionally, if your SPRS score is low, or if you have many missing security controls, you may need a consultant to develop a remediation strategy before moving forward.
4. Do You Need Help Implementing Technical Security Controls?
There are a range of technical security controls required by CMMC that many organizations may not have adopted yet. If your company lacks the bandwidth to deploy these measures, a CMMC consultant can provide guidance and support (or do it for you, depending on the level of support outlined in the engagement). These types of technical controls include configuring multi-factor authentication, implementing network segmentation, SIEM logging and monitoring, and vulnerability management.
5. Are You Prepared For A Third-Party or DoD Audit?
For Levels 2 and 3, organizations have to pass an official assessment conducted by a Certified Third-Party Assessor Organization (C3PAO) or the DoD. The most common issues contractors face with these assessments are due to insufficient documentation, improperly implemented controls, or lack of audit preparation. A CMMC consultant can remediate these issues and more in advance of your assessment.
6. Do You Need Ongoing Compliance Support?
Lastly, it's important to know that CMMC compliance requires ongoing monitoring and maintenance. You'll need to keep your certification in good standing year-round. If your organization does not have a dedicated team to handle continuous compliance, a CMMC consultant can provide long-term security and compliance management. Ongoing support can include:
- Review of your security controls
- Vulnerability scanning (and remediation as needed)
- Incident response drills
- Log reviews and SIEM tuning.
If the answer is "yes" to multiple questions, partnering with a CMMC consultant may be a good option for your organization.
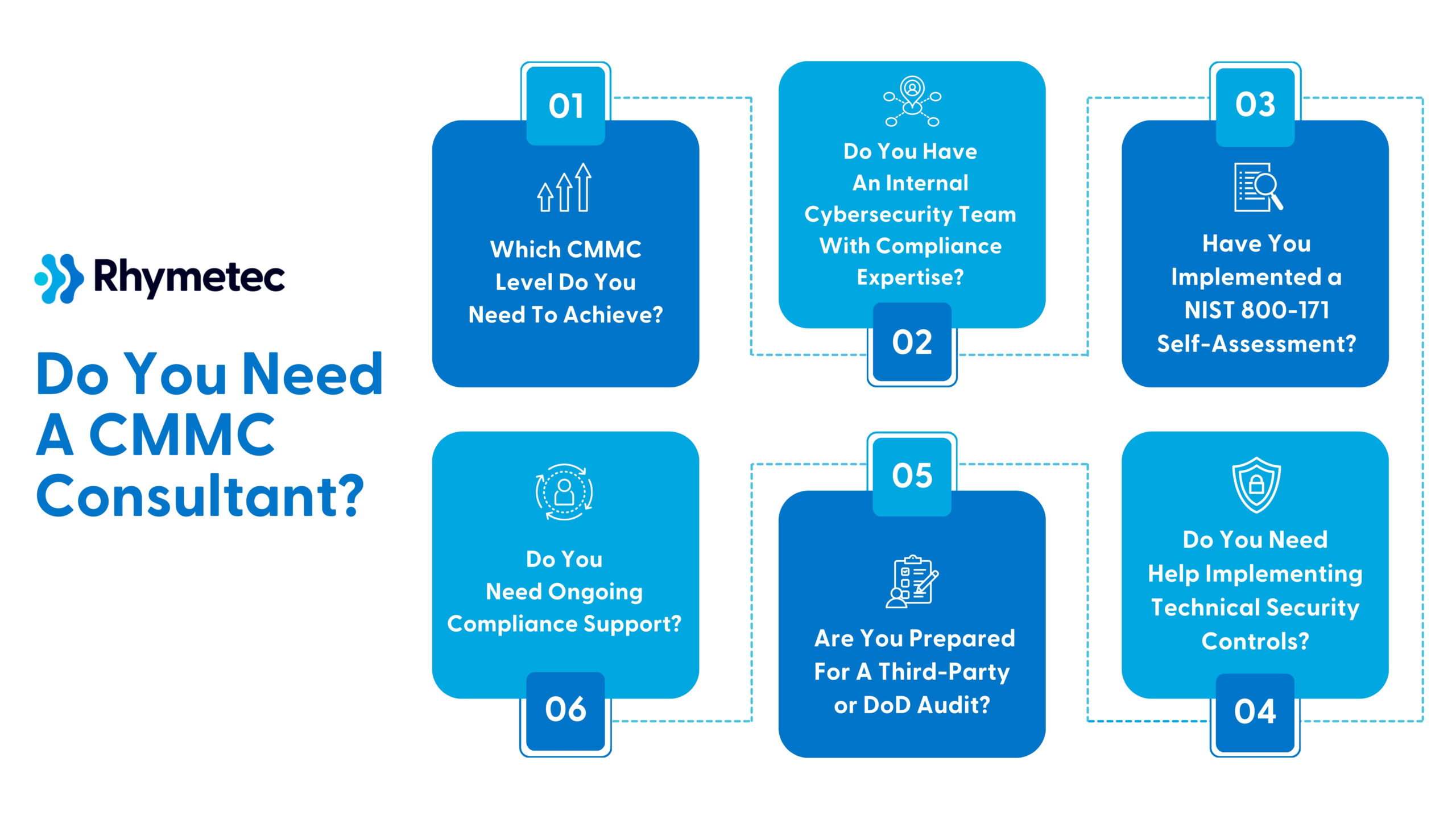
Next, let's go over what a CMMC consultant typically accomplishes for organizations throughout the engagement. This should help give you a good idea of what to expect:
Timelines And Deliverables From A CMMC Consultanting Engagement
A CMMC consultant provides end-to-end support to help defense contractors achieve CMMC compliance. At a high level, this process entails assessing your organization's current security posture, implementing the required controls you don't already have, developing documentation, training personnel, and preparing for the official assessment.
Here is what this process and the deliverables will look like, in general, for an organization starting from a more basic security posture:
1. CMMC Initial Assessment - Documentation and Gap Assessment:
- Conduct a gap assessment to assess your current CMMC maturity level.
- Review existing security documentation to determine alignment with CMMC 2.0. requirements and identify any gaps in your documentation to be addressed before certification.
- Review CUI/FCI data flows to assess how sensitive information is handled.
- Map current security controls to NIST SP 800-171 and CMMC requirements.
- Document your organization's Supplier Performance Risk System (SPRS) score.
- Develop a preliminary Plan of Action & Milestones (POA&M) to address deficiencies.
- Estimate resource requirements for remediation.
Timeline With A CMMC Consultant: 1-2 Months
2. Implementation of Access Control and System Security
- Configure multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all required systems.
- Implement least privilege access principles to restrict user permissions.
- Set up remote access controls and document access control procedures.
- Deploy a Privileged Access Management (PAM) solution for sensitive accounts.
- Implement network segmentation and develop network diagrams.
- Deploy endpoint protection solutions.
- Configure logging and monitoring systems, including SIEM solutions.
- Set up backup solutions and document backup and recovery procedures.
Timeline With A CMMC Consultant: 1-3 Months
3. Documentation and Policy Development
- Develop a System Security Plan (SSP) documenting security controls.
- Create an Incident Response Plan for handling security incidents.
- Establish a Disaster Recovery Plan.
- Create training documentation for security awareness and compliance.
Timeline With A CMMC Consultant: 1-2 Months
4. Training
- Conduct security awareness training for employees.
- Develop role-specific training for personnel handling CUI/FCI.
- Run incident response drills to prepare teams for cyber threats.
- Train employees on documentation procedures.
- Hold policy review sessions.
Timeline With A CMMC Consultant: 1 Month
5. Testing and Control Validation
- Perform internal control testing to verify compliance.
- Conduct vulnerability assessments and penetration testing to evaluate system defenses.
- Review security documentation for accuracy/completion.
- Validate processes and security controls through real-world testing.
Timeline With A CMMC Consultant: 1-2 Months
6. C3PAO Assessment
- Conduct a final documentation review to make sure all requirements have been met.
- Validate security controls against CMMC 2.0 standards.
- Prepare teams for staff interviews conducted during the official assessment.
- Perform technical testing to confirm systems meet all requirements.
Timeline With A CMMC Consultant: 1 Month
Ongoing Maintenance
To maintain compliance and readiness for recertification, a CMMC consultant provides ongoing support through the following:
- Monthly security control reviews to assess compliance status on an ongoing basis.
- Vulnerability scanning to identify and remediate emerging threats.
- Access reviews to ensure permissions remain properly restricted.
- Incident response testing to evaluate security team preparedness.
- Log review to monitor system activity and detect anomalies.
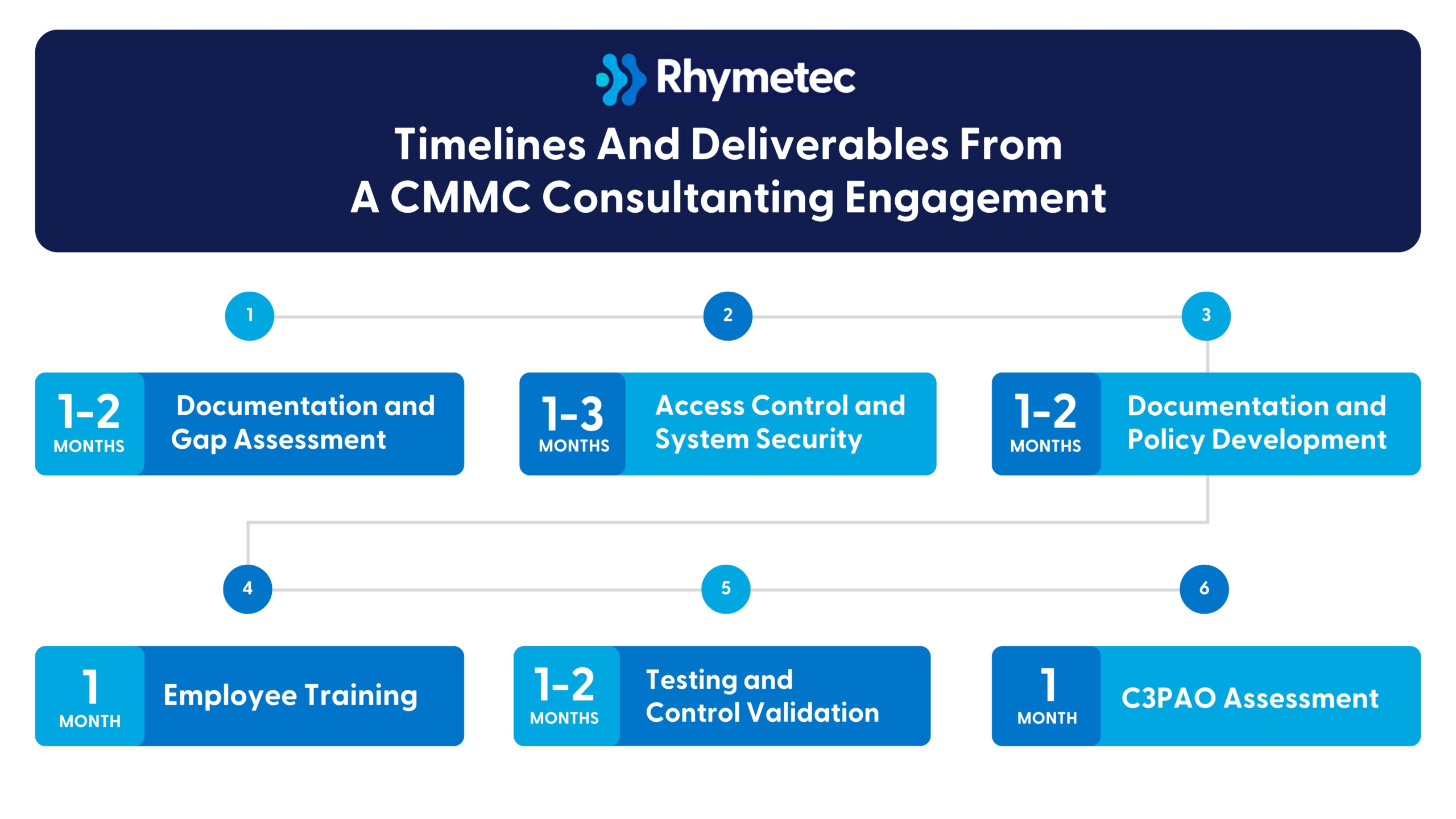
Why Work With A CMMC Consultant?
Achieving compliance is not simple. There is an array of technical and procedural controls and extensive required documentation. A CMMC consultant helps businesses navigate these requirements by providing specialized expertise (at a much lower price point than building out an in-house team would cost) and reducing administrative burdens.
Many defense contractors lack the in-house resources to manage requirements, especially as the DoD increases enforcement of cybersecurity standards. Often, for example, small defense contractors with no formal cybersecurity programs need to achieve CMMC Level 1 to continue bidding on DoD contracts. Having limited IT staff and a lack of security policies and policies can be a significant roadblock.
In this scenario, a CMMC consultant would help by starting with an initial assessment to determine the company's current security posture and documentation and, from there, develop all missing policies, procedures, and documents. Often, this includes a System Security Plan (SSP), access control policies, and an incident response plan.
Many contractors also underestimate the complexity of CMMC and wait too long to start the process. The risk of failing an assessment can lead to contract loss and reputational damage. Working with a CMMC consultant reduces risk, streamlines implementation, strengthens your cybersecurity, and ensures you stay audit-ready year-round.
If your business relies on DoD contracts, CMMC certification isn't optional. Engaging a CMMC consultant early on in the process saves significant time and headaches down the road.
About Rhymetec
Our mission is to make cutting-edge cybersecurity available to SaaS companies and startups. We’ve worked with hundreds of companies to provide practical security solutions tailored to their needs, enabling them to be secure and compliant while balancing security with budget. We enable our clients to outsource the complexity of security and focus on what really matters – their business. Contact us today to get started.
Interested in reading more? Check out more content on our blog.
As an industry leader in cybersecurity and compliance, Rhymetec is proud to partner with Vanta to deliver a complete solution for modern businesses. As Vanta's 1st MSP partner, together, we fast-track compliance, strengthen your security posture, and reduce the time and effort needed to meet regulatory requirements.
The Rhymetec + Vanta Advantage
Our team at Rhymetec leverages Vanta to transform compliance from a complex challenge into a strategic advantage for your business. Over the last decade, we've helped over 1,000 companies around the world meet their security and compliance goals.
With our joint services, you can:
1. Alleviate The Pressures of Audit Preparation
Vanta was built with auditors and the audit process top-of-mind. Rhymetec will ensure you have all the documents and evidence necessary for the audit itself, and manage the audit process using Vanta as a source of truth.
2. Access Continuous Security and Compliance Monitoring and Support
Vanta's automation capabilities help achieve ongoing compliance maintenance and management, while Rhymetec's vCISO services address ongoing security efforts and questionnaires, aiding new phases of growth.
3. Streamline Control Implementation With Vanta Compliance Services
Rhymetec implements controls required by the compliance framework selected by the client. Vanta plays a key role in this process for each control through system integrations and identification of areas for improvement.
Together, we provide a simplified approach to security and the compliance automation process. We work together to provide an automated and comprehensive solution, saving significant time and resources for you.
Our Vanta Compliance Services
Vanta Implementation and Deployment
Vanta automates 90% of compliance tasks through integrations with 300+ systems, real-time control monitoring, and automated evidence collection.
The Rhymetec team configures and deploys the platform on your behalf, integrating it with your infrastructure to maximize automation capabilities. We connect relevant systems, set up automated workflows, and customize policies to fit your organization and the selected compliance framework.
With Vanta deployment carried out by our experts, your team avoids the complexity of configuring integrations. From day one, we ensure accurate and reliable compliance monitoring and allow you to dramatically reduce the burden on your internal resources.
Compliance Framework Support From Start To Finish
Vanta provides pre-built controls for 20+ frameworks, including SOC 2, ISO 27001, HIPAA, and GDPR. It automates scoping and document management and provides a foundation for policy creation. The Rhymetec team aligns these automated capabilities with your business needs and your selected compliance framework, performing the tasks required for full compliance such as internal audits, tabletop exercises, and evidence preparation.
Managing compliance without a dedicated team can lead to missed controls or even doing too much and implementing unnecessary requirements. By handling the full compliance process, we eliminate uncertainty, accelerate your audit readiness, and ensure your documentation fully meets auditor expectations.
Continuous Optimization and Compliance Maintenace
Vanta's continuous monitoring identifies failing controls, missing security measures, and real-time compliance risks. Automated notifications provide alerts to potential issues, and remediation workflows drive fast resolution.
Our team at Rhymetec oversees these alerts, interprets risk impacts, and executes the manual corrections on your behalf so you can maintain compliance.
Ongoing compliance management is resource-intensive. Without expert oversight, organizations risk falling out of compliance between audits. With our team handling continuous monitoring and remediation, your organization stays audit-ready, reduces compliance drift, and proactively addresses any security gaps.
Penetration Testing To Meet Audit and Regulatory Requirements
Many voluntary frameworks as well as legal requirements require penetration testing.
SOC 2, PCI DSS, ISO 27001, CMMC, and HIPAA all include requirements to regularly test network and application security. Regulations such as GDPR and CCPA also encourage proactive security measures to identify vulnerabilities before a security incident can occur, and penetration testing can be used to fulfill these requirements.
Rhymetec started as a penetration testing company in 2015, and we offer the highest quality penetration tests to meet your organization's compliance obligations while enhancing its security posture. We provide detailed reports of the findings, along with remediation recommendations, helping your organization address security gaps before an audit.
We offer a range of penetration testing services to fit your security and compliance needs, including mobile application penetration testing and web application penetration testing.
Strategic Security Guidance
Vanta's AI-driven features streamline core compliance areas to include risk management, access reviews, vendor security assessments, and security questionnaires. The platform accelerates compliance workflows, while expert guidance from Rhymetec's team enables you to interpret findings, implement security best practices, and customize controls based on your unique risk profile and risk appetite.
Security and compliance strategies must be tailored to business needs. Without in-house expertise, it can be difficult to implement effective controls. With Rhymetec's team providing ongoing guidance, while leveraging Vanta's cutting-edge integrations and capabilities, you gain a compliance program that meets regulatory requirements while reducing risk to your organization and maintaining operational efficiency.
Why Rhymetec?
Transparency:
We believe our clients deserve complete clarity about what they're getting, how we work, and the results they can expect. Whether it's our methodologies, testing scope, or the tools we use, we provide detailed insights at every step.
Autonomous:
As a self-funded company, we have the freedom to make client-focused decisions quickly and flexibly. This independence allows us to adapt our services to meet your unique needs and help our partners win in competitive scenarios. Our autonomy ensures every decision prioritizes your success.
Team Credentials:
Our team boasts a broad range of industry-recognized certifications, including Burp Suite Certified Practitioner, ISC2 CISSP, EC-Council CHFI, CPENT, Offensive Security: OSE3 OSED OSEP OSWA OSWE OSCP, and CompTIA Security+, PECB Internal Auditor Certifications, and more.
Market Maturity:
Rhymetec was founded in 2015. Our specialized expertise ensures a deeper understanding of your business's unique challenges, providing the most impactful security insights. Don't settle for less experienced competitors when it comes to protecting your business or meeting the needs for compliance requirements.
Frameworks Supported by Rhymetec's Vanta Compliance Services
Achieve compliance faster and with greater confidence with Vanta's automation and Rhymetec's hands-on security expertise. Together, we streamline control implementation and tackle every step of the compliance process for you. We fully manage the following frameworks (and more) on your behalf, from start to finish, getting you over the finish line with your audit in the fastest time frame possible:
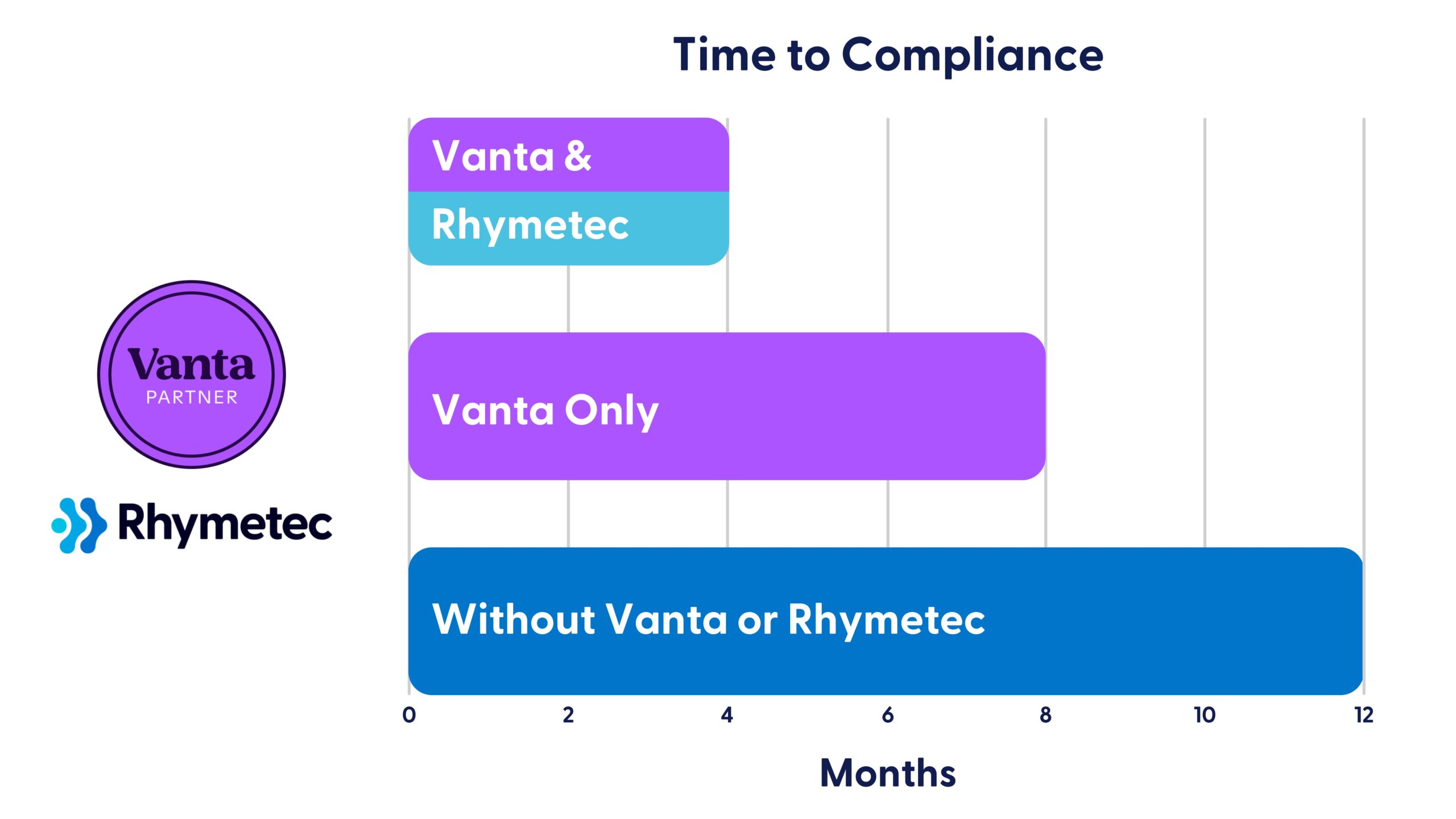
SOC 2 With Vanta & Rhymetec
Vanta automates control monitoring, policy management, and evidence collection for SOC 2, reducing the time required to prepare for an audit. As SOC 2 allows flexibility in control implementation (which requires interpretation to align with your business operations), the Rhymetec team ensures that automated controls are properly scoped, fills in gaps with manual tasks like risk assessments and penetration testing, and guides your team through audit readiness.
ISO 27001 With Vanta & Rhymetec
Vanta accelerates ISO 27001 certification by automating risk assessments, system inventory, and document management, including the Statement of Applicability. ISO 27001 also requires internal audits and ongoing security improvements. Our team at Rhymetec handles these manual components and others, develops custom policies, and aligns your Information Security Management System (ISMS) to your business risks.
GDPR
Vanta supports GDPR compliance through automated access reviews, vendor risk assessments, and security monitoring. GDPR compliance also entails implementing legal and operational processes, such as data mapping, incident response planning, Data Protection Impact Assessments, and more. At Rhymetec, our vCISOs carry out these actions and ensure that all of your privacy policies, manual risk assessments, and data processing agreements are in full alignment with GDPR requirements.
HIPAA
Vanta automates HIPAA compliance by monitoring technical safeguards, conducting access control reviews, and managing security policies. For the aspects of HIPAA compliance that require administrative safeguards, such as employee training, documented risk management procedures, and business associate agreements, the Rhymetec team bridges the gap by filling in or fine-tuning these items. For example, we implement customized employee training and advise you on regulatory expectations. Leveraging Vanta and our services provides a complete approach to HIPAA compliance.
PCI DSS
Vanta identifies security gaps related to PCI DSS controls, while the Rhymetec team fills pieces such as penetration testing, network segmentation, and quarterly scanning. Our experts ensure that all PCI DSS requirements are met, manages security assessments, and handles auditor interactions for you. By combining Vanta's automation with our technical security expertise, you meet the requirements in the fastest timeframe possible and maintain continuous compliance over time.
CMMC
Vanta helps streamline CMMC compliance by automating areas such as security control monitoring and access review. While working to meet the extensive CMMC requirements under risk management, ongoing assessments, and security controls, a dedicated team of security and compliance experts can greatly reduce the complexity for your organization. While leveraging Vanta, Rhymetec’s team ensures that all necessary security measures (including incident response planning tailored to your organization, system security plans, and third-party risk management) are correctly implemented.
Additional Frameworks Supported By Rhymetec and Vanta
Beyond the frameworks listed above, Vanta and Rhymetec support a range of other compliance frameworks. These include ISO/IEC 42001 for AI risk management, DORA for financial sector resilience, HITRUST CSF for healthcare security, NIST AI RMF for AI governance, The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and various other global and industry-specific standards.
For any framework(s) you select, using Vanta in conjunction with Rhymetec's guidance streamlines certification, strengthens your security operations, and sets you up for successful long-term compliance.
Ready to Simplify Your Vanta Compliance Journey?
Don't let compliance barriers slow down your growth.
Our experts are ready to transform security from a roadblock to a competitive advantage. We leverage the most cutting-edge tools like Vanta on your behalf and remove the work entirely off your plate so you can get back to what really matters - running your business. Contact us today to learn more.
About Rhymetec
Our mission is to make cutting-edge cybersecurity available to SaaS companies and startups. We've worked with hundreds of companies to provide practical security solutions tailored to their needs, enabling them to be secure and compliant while balancing security with budget. We enable our clients to outsource the complexity of security and focus on what really matters – their business. Contact us today to get started.
Interested in reading more? Check out more content on our blog.
Needing to meet EU AI Act compliance has further complicated regulatory requirements around AI for many companies - even those that are located outside of Europe. The stakes are substantial, with fines of up to €35 million or 7% of global annual revenue for serious violations. For context, that exceeds even GDPR penalties.
The Act imposes significant obligations on companies developing or deploying AI systems. If you're a U.S.-based SaaS company offering AI-powered services in the EU, for example, the law may apply to you. If your product touches high-risk areas like healthcare, recruitment, or finance, you'll have stricter protocols to follow.
Our team at Rhymetec helps organizations understand their compliance requirements, automate the parts of compliance that can be automated, and fast-track your compliance. This article will help you understand whether your AI systems fall within scope and their risk categories, the measures you need to implement, and how to turn compliance into a competitive advantage.

Which Types of Organizations Need EU AI Act Compliance?
The EU AI Act applies to organizations that develop or use AI systems within the European Union (EU), regardless of where they are based. Even companies outside of the EU must comply if their AI systems affect individuals in the EU.
The Act categories AI systems based on risk, with corresponding requirements for each category:
- Prohibited AI Systems: These are AI systems that pose unacceptable risks. An example of this under the EU AI Act would be an AI system being used to predict the risk of an individual committing a crime based solely on personality or profiling traits.
- High-Risk AI Systems: AI used in critical areas such as law enforcement, hiring, credit scoring, infrastructure, and medical devices must meet strict requirements. Both providers and deployers of high-risk AI have to comply with these obligations.
- Limited-Risk AI Systems: AI systems with transparency obligations, such as chatbots or AI-generated content, must disclose that users are interacting with AI.
- Minimal-Risk AI Systems: These are AI applications with low regulatory impact, such as spam filters or recommendation algorithms. These tend to be largely unaffected by the EU AI Act.
Organizations impacted by the AI Act include:
- AI Developers and Providers: Companies building AI models or integrating AI into their products must meet compliance requirements if their systems fall under high-risk or transparency rules.
- Deployers of High-Risk AI: Businesses using AI systems classified as high-risk in hiring, credit decisions, or critical services must comply with risk management and oversight obligations.
- Distributors and Importers: Organizations that place AI systems on the EU market must verify compliance before distribution.
- Non-EU Companies Serving EU Users: Organizations are subject is the Act if they offer AI-driven services or products affecting EU individuals. For example, a software company outside of the EU selling AI-based medical diagnostics to European healthcare providers would need to comply.
Companies must determine which of their AI systems fall under the AI Act's scope and what compliance obligations apply, based on how the technology is being used.
What Are The Requirements, and How Can EU AI Act Compliance Be Achieved?
Compliance with the EU AI Act entails several core requirements (all of which Rhymetec can fulfill on your behalf!). Below are the main requirements and how to meet them. Keep in mind that your organization's requirements will vary based on the risk level of your AI systems, as discussed above.
1. Risk Management
High-risk AI providers are required to extensively document their risk management process. Risk management under the EU AI Act means having a clear process on how you will assess and mitigate AI-related risks, through measures including continuous monitoring and periodic evaluations to address any emerging risks.

2. Incident Response and Business Continuity
Organizations must have mechanisms in place to not only identify AI risks but also to actually respond to incidents.
Your team should know exactly how they would respond and recover from AI-related failures or security incidents. This can be documented in an incident response plan, which is a good idea for every organization to have regardless of their compliance obligations. For your business continuity plans, the goal should be to ensure that AI systems remain operational and safe during disruptions.
3. Data Protection and Recovery
AI systems must use training data that is as high-quality and unbiased as possible. They must also implement corresponding controls to protect data from unauthorized access, corruption, or loss. This set of requirements under the EU AI Act shares heavy overlap with privacy regulations in the EU, such as GDPR.
4. Ongoing Security Controls
AI systems need to include safeguards against cybersecurity threats and vulnerabilities. This can be accomplished by applying security measures, including access controls, logging, and anomaly detection.
5. Compliance Documentation and Reporting
Lastly, AI providers need to keep detailed records of system design, functionality, and decision-making processes. High-risk AI systems require additional technical documentation that can be reviewed by regulators.
How Does The EU AI Act Compare To Voluntary AI Frameworks?
Understanding the differences and overlap between the EU AI Act and voluntary frameworks (like ISO 42001 and the NIST AI Risk Management Framework) can help streamline your compliance efforts. The good news is that these frameworks do overlap quite a bit, and you can leverage existing work you may have already completed and/or use EU AI Act compliance to fill in requirements for future regulations.
The EU AI Act vs. ISO/IEC 42001
ISO 42001 provides an excellent framework for AI governance but does not carry legal obligations. Companies that adopt ISO 42001 must still meet the EU AI Act's legal obligations if their AI system(s) fall under the Act. Fortunately, there is some overlap between the EU AI Act and ISO 42001 controls:
If your organization already has an ISO 42001-compliant risk management framework, it can fairly easily be adapted to fulfill the EU AI Act's risk assessment obligations. Both the EU AI Act and ISO 42001 also include controls for bias mitigation and improving data quality. If you have already documented data governance policies under ISO 42001, they can contribute to meeting these requirements.
Finally, ISO 42001 requires documenting your AI system risks and objectives. The AI Act mandates similar documentation for high-risk AI systems, so an organization that is already ISO 42001 compliant can leverage existing documentation to fulfill the AI Act's record-keeping obligations.
The EU AI Act vs. The NIST AI Risk Management Framework
The NIST AI RMF is a voluntary guideline that provides a framework organizations can use to manage AI risks, but it does not entail enforcement measures or assign risk categories.
However, both heavily emphasize risk management and governance. Companies that have already adopted the NIST AI RMF already have elements in place that align with the AI Act requirements. For example, the NIST AI RMF defines oversight roles that can be mapped onto the AI Act's requirements to designate responsible individuals for compliance and monitoring.
Another area in which the requirements overlap is transparency and documentation. Under the NIST AI RMF, organizations are encouraged to document AI risks and decision-making processes. Likewise, the AI Act requires technical documentation for high-risk AI systems, including explanations of system functionality.
In general, businesses with existing voluntary AI frameworks can accelerate EU AI Act compliance by mapping existing controls to the Act's requirements. Organizations that use the NIST AI RMF or ISO 42001 have a head start in EU AI Act compliance, but must still determine whether their AI system(s) fall under the Act and what additional legal obligations apply.

5 Business Benefits of EU AI Act Compliance
For many organizations, complying with the EU AI Act is a regulatory requirement. However, it can also provide other advantages. Companies that integrate AI Act compliance into their operations reduce their legal risks while strengthening their market position and improving trust. The 5 main benefits are:
1. Broader Access To The EU Market
Compliance allows businesses to sell and deploy AI systems in the EU without facing legal barriers or enforcement actions. Companies that fail to comply, meanwhile, risk facing fines and restrictions on their AI products.
2. Substantial Reduction in Risk To Your Organization
By implementing AI governance, risk management, and transparency measures, you can reduce the likelihood of legal disputes, regulatory penalties, and reputational damage to your organization.
3. An Advantage Over Non-Compliant Competitors
By meeting the requirements under the EU AI Act, your organization can demonstrate a commitment to responsible AI use, which helps differentiate you in the market. Customers, investors, and business partners may prioritize vendors with compliant AI solutions.
4. Stronger AI Governance
A natural byproduct of meeting requirements under the EU AI Act is having clearer AI-related policies and oversight processes. This improves internal decision-making and AI systems' reliability. Companies that comply with the EU AI Act will also find it easier to adapt to other current and/or future AI regulations.
5. Customer and Public Trust
The general public and businesses are increasingly concerned about AI-related risks. Seeing that you are compliant with the EU AI Act creates reassurance that you take the risks seriously, and builds confidence in your AI products and services.
In Conclusion: EU AI Act Compliance Key Takeaways
The EU AI Act introduces an array of requirements impacting AI providers, deployers, and businesses operating in the EU or serving EU users. Compliance includes risk management, incident response plans, documentation, and ongoing security controls. EU AI Act compliance is an entry point to many business advantages, such as expanding your market access in the EU.
Many organizations choose to outsource the work of EU AI Act compliance to a virtual CISO (Chief Information Security Officer). Our virtual CISOs at Rhymetec have helped over 1,000 organizations meet their security and compliance needs in the fastest timeframe possible. Contact us today or check out our information on vCISO pricing to learn more.
Interested in reading more? Check out more content on our blog:
- DORA Compliance Checklist: What The EU's Digital Operational Resilience Act Means For Your Business
- NIS2 Requirements: What You Need To Know For Your Business
- Compliance For Startups: The Definitive Guide to Picking the Right Consultant
Meeting NIS2 requirements can be complex regardless of organizational size, especially the requirements around managing third-party risks and incident response. In this article, we go over what NIS2 requires, how to avoid penalties, and how to leverage the requirements to support business growth and operations.
The NIS2 Directive represents another new requirement in an increasingly strict cybersecurity regulatory ecosystem. The law, which came into force in January of 2023, specifically impacts organizations operating in the European Union (EU). Businesses that provide essential or important services must meet the obligations or face regulatory scrutiny.

What Is NIS2?
NIS2 is the EU's updated cybersecurity Directive, expanding on the scope of the original NIS Directive to cover more sectors and introduce even stricter security, risk management, and reporting requirements. If your business provides services in the EU ranging from transportation, banking, healthcare, manufacturing, food production, and more, you are likely required to comply.
The Directive applies to industries including technology, finance, healthcare, energy, and transportation, as well as many digital service providers. Broadly, it requires organizations to implement risk management measures, report significant incidents within 24 hours, and effectively manage third-party risks.
Non-compliance can result in fines of up to €10 million or 2% of global annual turnover, whichever is higher. Compliance impacts not only your regulatory standing but also your contracts, customer trust, and business continuity. Building a compliance strategy early will help avoid last-minute disruptions and potential penalties.
Who Must Comply With NIS2 Requirements?
NIS2 applies to organizations classified as essential or important entities across a variety of sectors. The Directive expands largely on the scope of the original NIS Directive, covering a broader range of industries and lowering the threshold for organizations that must comply.
Essential entities include large organizations in critical sectors where cybersecurity failures could have widespread and serious impacts, such as:
- Energy - Electricity suppliers, gas providers, oil companies, and district heating operators.
- Transport - Airlines, rail operators, shipping companies, and logistics providers.
- Banking - Credit institutions and financial market infrastructure providers.
- Healthcare - Hospitals, clinics, and pharmaceutical manufacturers.
- Drinking Water & Wastewater - Water supply and treatment facilities.
- Digital Infrastructure - Cloud services providers, data center operators, and domain name system (DNS) service providers.
Important entities are medium and large businesses in sectors that are critical but do not require the same level of regulatory scrutiny. These include:
- Manufacturing - Producers of medical devices and electrical equipment.
- Food Production - Businesses that manufacture food and beverages.
- Postal and Courier Services.
- Waste Management Companies.
- Digital Service Providers - Online search engines, marketplaces, and social networking platforms.
- Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) - Businesses providing cybersecurity services to other organizations.
It's important to note that both essential and important entities are generally defined as medium or large enterprises, meaning they have at least 50 employees or an annual turnover of €10 million or more. Smaller organizations, however, may still fall under NIS2 if they are critical to a supply chain or if they operate in a high-risk sector.

NIS2 Requirements: What You Need To Plan For
NIS2 entails a range of security and operational requirements, with a particular emphasis on minimizing cybersecurity risks. Below is an explanation of the 5 overarching requirements and what implementing them may look like for your organization.
1. Risk Management & Security Measures
NIS2 requires organizations to take a proactive approach to mitigate cybersecurity risks.
Security measures across areas, including network security, data protection, and system integrity, are required. Here's what this may look like in practice for your organization, particularly if you are a SaaS company:
- Implementing Access Control Measures: Access control measures such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all employees and users accessing your platform are required under NIS2. MFA means both a password and app-based token or another second form of verification are needed to log in.
- Enabling Data Encryption Measures: Encrypt sensitive customer data both at rest and in transit. For NIS2, this includes encrypting databases and using TLS (Transport Layer Security) for all data exchanged between clients and your platform.
- Creating A Patch Management Program: Regularly update software and systems to fix vulnerabilities. Additionally, you'll need to implement an automated patching system that ensures no critical updates are missed.
- Conducting Regular Vulnerability Scanning: This requirement entails using automated tools to regularly scan your applications and infrastructure for vulnerabilities. For instance, using tools like Nessus can identify weaknesses.
2. Incident Reporting Obligations
NIS2 mandates relatively quick reporting of cybersecurity incidents in the event they occur. As an example, if you were to experience a breach where an attacker gained access to customer data, you would be required to notify relevant authorities and affected clients within the prescribed timeframe and provide updates on the breach as it is resolved.
In practice, setting up the incident reporting process from beginning to end will likely entail the following for your organization:
- Creating An Incident Response Plan: Internal incident response policies that outline the exact steps to take when a breach occurs, designate a response team, and describe how you will identify the root causes of the breach are required.
- Setting Up Incident Detection Tools: Set up monitoring systems like SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) to detect unusual activity in real-time. Tools like Splunk or Datalog track suspicious logins or data exfiltration are commonly used for this purpose.
- Making A Plan To Follow Compliance with Reporting Deadlines: Lastly, know what your process would be for reporting incidents in a timely fashion to the appropriate authorities and your affected clients.
3. Governance & Accountability
An increasing emphasis on governance is being seen across historically gold standard cybersecurity frameworks such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (NIST CSF) with the addition of the NIST governance function. This shift is being seen in recent laws as well, including in the case of NIS2.
In practice, this means that cybersecurity should not be a function of just IT, but a function of corporate governance and should stem from there. Senior management is responsible for making sure that the organization meets NIS2's cybersecurity requirements and that sufficient resources are allocated. Leadership must:
- Appoint Cybersecurity Leadership: Appoint a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) or designate a cybersecurity lead who will be accountable for ensuring the organization meets NIS2's requirements.
- Ensure Employee Training is Conducted: Employees, particularly those who handle sensitive data, need to be trained in cybersecurity practices and incident reporting procedures. This often takes the form of having mandatory, recurring cybersecurity awareness sessions, phishing training for employees, and/or tabletop exercises.
- Receive Board-Level Reporting: Senior management should regularly receive reports on cybersecurity risks and incidents, and be involved in decision-making processes related to cybersecurity investment. This can take the form of discussing the current cybersecurity posture and resource allocation at quarterly board meetings, for example.
4. Third-Party Risk Management
NIS2 puts the obligation on businesses to manage risks posed by their third-party vendors, especially if those vendors provide business-critical services or have access to sensitive data. A third-party risk management program entails the following elements:
- Vendor Risk Assessments: A vendor risk assessment evaluates the security and compliance practices of third-party providers. This is especially important for vendors that provide services such as cloud hosting, payment processing, or customer support. These vendors and others need to be able to show they meet NIS2's security standards.
- Third-Party Contracts: Contracts with vendors need to define their security obligations (requiring them to comply with certain security standards, report incidents within specific timeframes, and/or undergo audits of their security practices). Your contract for your cloud provider, for example, should outline measures they need to have in place, such as strong access controls and encryption.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Continuously monitoring your vendors. For instance, regularly review their security certifications, check they are staying compliant with relevant laws or frameworks, or conduct periodic assessments.
5. Compliance & Auditing
NIS2 requires maintaining evidence of your cybersecurity practices, with measures such as:
- Internal Audits: Periodic internal audits of security practices to ensure compliance maintenance with NIS2. Internal audits service to verify that measures like encryption and access control are functioning as intended.
- Risk Assessment & Incident Reports Documentation: Keeping up-to-date records of risk assessments, incident reports, and audits helps meet NIS2's governance and accountability requirements.
- External Audits: In some cases, if an organization falls within the essential or important entity categories and is subject to supervisory measures by national authorities, it may be required to undergo an external audit. Some jurisdictions may also require routine external audits for critical infrastructure or high-risk organizations.
NIS2 Requirements: 5 High-Level Requirements
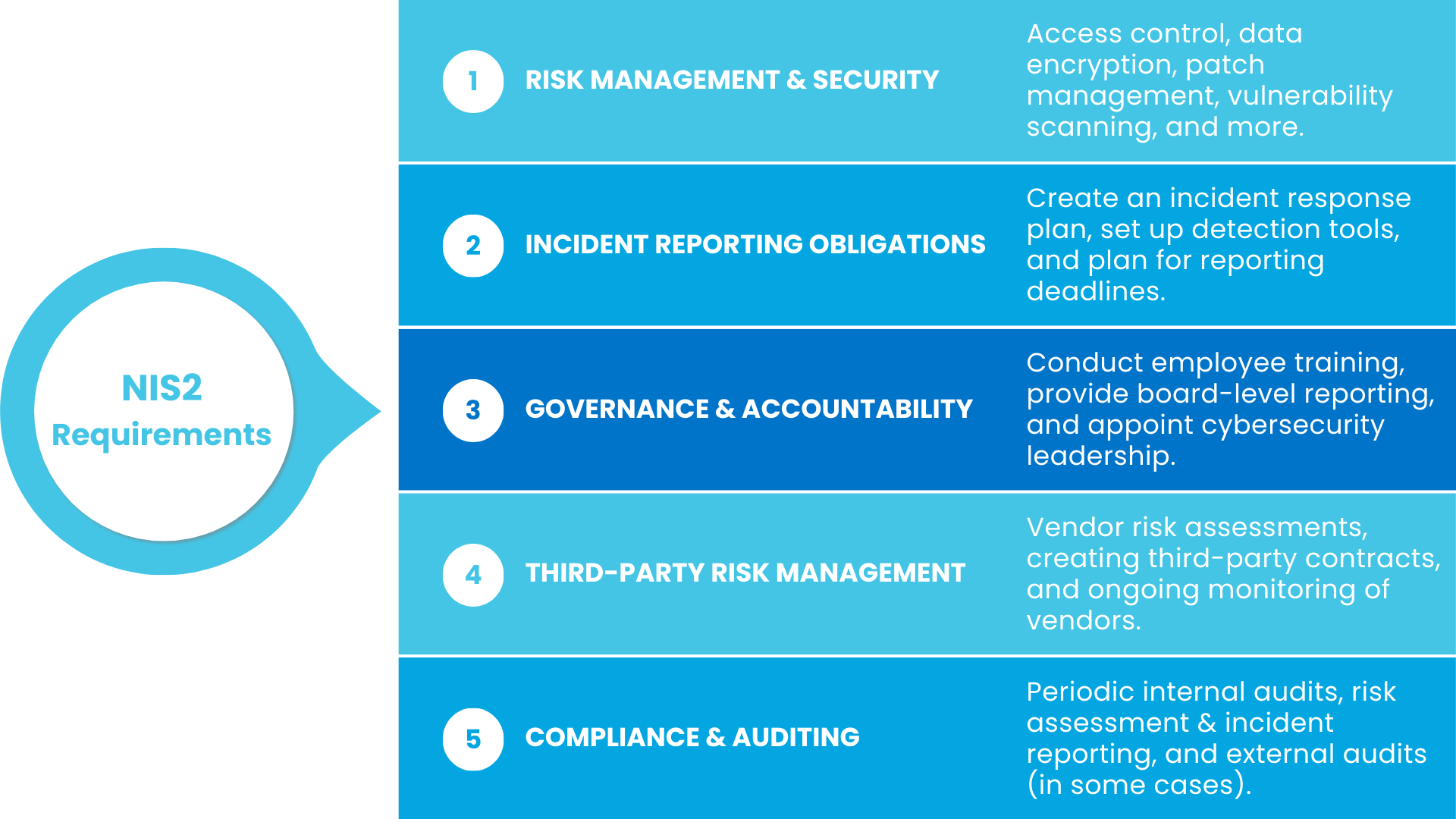
Meeting NIS2's requirements will involve a combination of technical measures, governance practices, and ongoing actions such as continuous monitoring. For organizations like SaaS startups, implementing these requirements ensures you are in compliance with the law and are well-equipped to build a secure platform that protects user data and reduces business risks.
How NIS2 Affects Third-Party Relationships
NIS2 expands security obligations to include third-party vendors and service providers, requiring businesses to manage risks introduced by their supply chain. Practically, this means you must verify that your vendors (including cloud services providers and software vendors) meet security standards and comply with contractual requirements.
With NIS2, due diligence with your vendors' cybersecurity practices is especially important as organizations covered by NIS2 are responsible for security incidents linked to their third parties.
A common way to verify your vendors' security is by requesting to see evidence of their compliance with cybersecurity frameworks and laws relevant to your industry and location. Security questionnaires, audits, and contractual clauses can also be used to clarify your vendors' security practices. However you choose to accomplish this, third-party relationships need to be documented as part of your overall risk management efforts.
Vendor agreements need to set clear security expectations, incident reporting obligations, and liability terms. Due diligence and ongoing monitoring can help identify risks before they lead to regulatory penalties or operational disruptions.

How Do NIS2 Requirements Compare To Other Cybersecurity Regulations In Terms Of Third-Party Risk?
NIS2 places an even stronger emphasis on third-party risk management compared to many other cybersecurity regulations.
Here's how it compares to a few major frameworks:
NIS2 vs. NIS1
The focus on third-party risks is, in fac,t the most substantial change between NIS2 vs. NIS1. NIS1 focused more on internal security measures without expansive supply chain obligations. NIS2, however, expands on the original NIS Directive by explicitly requiring organizations to assess and manage third-party risks.
NIS2 vs. GDPR
GDPR compliance requires third-party risk management in terms of data protection and requires organizations to have contracts with processors handling personal data. NIS2 goes a step further and requires security risk assessments, continuous monitoring, and contractual obligations for security, even for vendors that don't process personal data.
NIS2 vs. ISO 27001
ISO 27001 includes third-party risk management as part of an overall information security management system (ISMS). However, compliance is voluntary. NIS2, meanwhile, mandates risk management practices for third parties and includes enforcement actions for non-compliance.
NIS2 vs. DORA
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA), which applies to financial services organizations, actually has stricter third-party risk requirements than NIS2. DORA requires direct regulatory oversight of critical third-party providers. NIS2 requires strong vendor risk management, but an important distinction is that it does not impose direct regulatory supervision on suppliers.
Where To Start
After you understand whether your organization is in scope and what gaps exist in your current security program, the next step is to develop a compliance plan and begin implementation (see the section above on NIS2 Requirements for what you'll need to plan for).
A popular option for many organizations nowadays is to work with a virtual Chief Information Security Officer (vCISO) at this stage. A vCISO helps translate NIS2 requirements into a plan specifically made for your business. They provide the expertise needed to interpret requirements, assess your risks, and build a compliance roadmap, all without incurring the cost of a full-time security executive or having to build out an in-house team.
Compliance automation tools, which automate risk assessments, track your security controls, and generate documentation, can also vastly simplify the process. Our vCISOs at Rhymetec leverage compliance automation tools on behalf of our clients while also completing all of the manual security work needed to meet requirements.
About Rhymetec
Our mission is to make cutting-edge cybersecurity available to SaaS companies and startups. We've worked with over 700 companies to provide practical security solutions tailored to their needs, enabling them to be secure and compliant while balancing security with budget. We enable our clients to outsource the complexity of security and focus on what really matters – their business. Contact us today to get started.
Interested in reading more? Check out more content on our blog.