This ISO 42001 checklist will walk you through the four phases of achieving certification.
These steps are based on our security team's process for helping organizations complete their ISO/IEC 42001 certification readiness. Our security team at Rhymetec has helped hundreds of companies achieve their security goals and meet compliance requirements. To find out how we can fast-track you to ISO 42001 compliance, contact our team today:
Hopefully, this checklist will give you a clear idea of the work ahead needed for ISO 42001 compliance and will help you create a project plan.
We'll start with a high-level overview of your ISO 42001 checklist and then dive into each phase in detail:

ISO 42001 Checklist Overview
1. Build a Strong Base for ISO 42001 Compliance.
- Understand Your ISO 42001 Requirements
- Conduct An Initial Gap Analysis
- Conduct A Risk Assessment
- Obtain Executive Support
2. Execute Your ISO 42001 Compliance Blueprint.
- Designate a Compliance Project Leader
- Draft An Implementation Roadmap For AIMS
- Set Up The AIMS Structure
- Create Organization-Wide Awareness
- Apply Necessary AIMS Controls
- Conduct Executive AIMS Evaluations
3. Preparation for Your External Audit.
- Conduct Internal Audits
- Select an ISO 42001 Certification Body
- Prepare Documentation
- Pre-audit Meeting
4. Obtain Your Certification.
- Undergo Your Audit
- Address Any Identified Issues
- Ongoing Improvements & Post-Audit Plan
Let's go over detailed steps under each phase:
Phase 1: Build A Strong Base For ISO 42001 Compliance
In this phase, you'll lay the groundwork for your organization to build an Artificial Intelligence Management System (AIMS) and achieve ISO 42001 compliance.
Establishing an AIMS is not just about compliance; it's about crafting a concrete strategy to improve decision-making and risk management around AI technologies. After this phase, you'll have a clear direction for responsible AI use and be on the right path to work towards ISO 42001 compliance:
1. Understand Your ISO 42001 Requirements
Does your organization act as a producer, provider, or user of AI systems?
You'll have different requirements depending on which of these your organization falls under.
Providers are companies such as OpenAI that build AI models like ChatGPT. Service providers customize and use these models. Users can include any business that uses AI services either directly from producers or via services from providers.
Which AI systems, processes, and technologies will your AI Management System cover?
Which technologies and assets do you have that incorporate AI? You will need to identify what will be included to map out the boundaries of your Artificial Intelligence Management System (AIMS).
Make sure you understand AI concepts as established in ISO frameworks.
Are you already familiar with how ISO frameworks define terms like "AI systems" and "machine learning models"?
If so, great! If not, ISO provides a glossary of terms you can use to see exactly what the frameworks mean when they use these terms. It's important to familiarize yourself with the terminology to understand each step of the compliance process, speak the same language as your auditors, and avoid miscommunications.
2. Conduct An Initial Gap Analysis
Evaluate your current ISO 42001 controls.
Compare your existing practices against ISO 42001 controls. Do you have any current practices to mitigate AI risks? What about ethical concerns related to AI, and data integrity concerns? You may already have a basis for some of the controls, especially if you already have another ISO framework.
Identify where you need to develop new controls or adjust existing ones.
Now that you have an idea of how your current practices map onto ISO 42001 controls, draft up a complete list of what you need to do to develop new controls or adjust existing ones. You will need this going forward.
3. Conduct A Risk Assessment
Identify all potential hazards associated with AI systems and development.
Unlike frameworks like ISO 27001, ISO 42001 does not focus heavily on security.
Security is an element of the framework, but a relatively small one. Instead, the potential hazards associated with AI, such as ethical issues, environmental considerations, and concerns around fairness and bias, are key.
Focusing on the areas mentioned above, come up with a list of potential AI risks related to your products, services, and all other activities.
Prioritize risks based on their level and determine corresponding controls.
Assess the likelihood and potential consequences of each risk. You will need this documentation later on. Start drafting an action plan to remediate risks, focusing on the highest risks first. Assess your list of existing practices and their effectiveness in mitigating risks.
Threats range from cybersecurity attacks to operational risks like system failures or errors in the AI's decision-making process. For each AI-related risk that your organization could potentially encounter, the impact level needs to be assessed:
Impact is categorized as low, medium, or high based on factors like financial loss, legal repercussions, and damage to customer trust. As an example, if your AI handles sensitive or critical data, the risk of a data breach would be considered high risk (as a breach could result in substantial legal and reputational damage).
A medium risk could be data bias in functions that are not critical to core operations but could impact user satisfaction or minor decision-making processes. A threat with a low-risk level could be any potential minor AI performance fluctuations. If you use an AI-driven customer support chatbot, for example, the risk of users experiencing minor delays in response time or slight inaccuracies in non-critical responses could be considered low risk.
Think ahead when conducting your risk assessment: What would happen if your organization experienced each risk? How complex would remediation be? How would employees, stakeholders, and your business operations be impacted?
4. Obtain Executive Support
Build a business case for ISO 42001 certification.
Create a compelling business case that shows the strategic benefits of ISO 42001 certification. Include how it will enable AI governance, help your organization comply with regulations, ease concerns that customers and prospects may have, and build stakeholder trust.
A formalized AI management system offers a lot of long-term value. What this looks like will depend on your specific organization. Try to emphasize not only the ways in which ISO 42001 mitigates risk but also how it offers opportunity and innovation potential.
Assign responsibilities to senior management for AIMS.
Assign senior management responsibilities to align the AIMS with your goals and provide them with the necessary resources.
Engage department heads in the analysis.
Bringing in department heads from IT, legal, operations, and human resources into the gap analysis process, for example, is a great way to create engagement across the organization. Plus, their involvement ensures all potential impacts of AI systems are being considered.
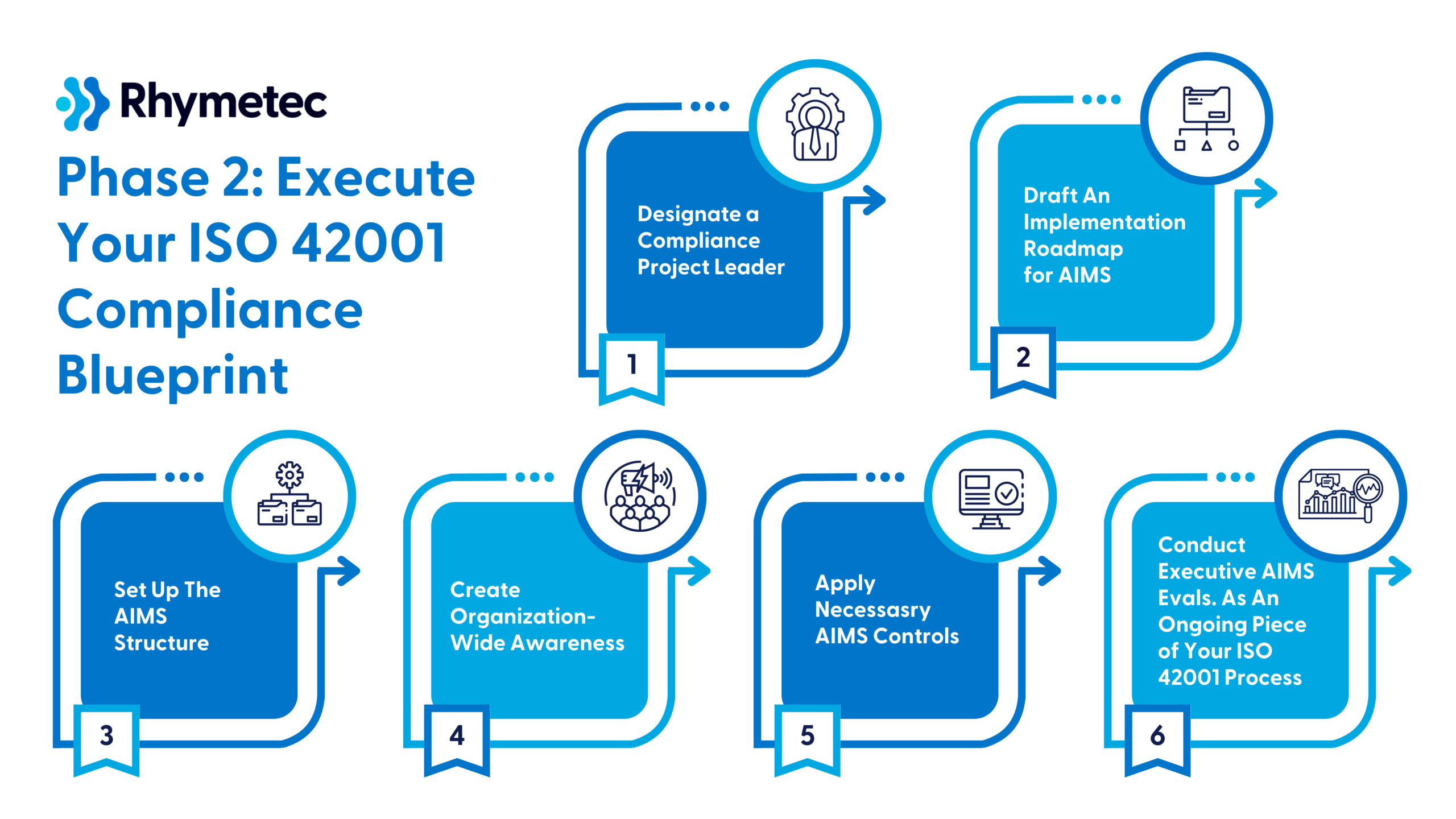
ISO 42001 Checklist Phase 2: Execute Your ISO 42001 Compliance Blueprint
Here, you'll activate the plans laid out above. This phase involves hands-on tasks such as appointing a project manager, setting up the structures for your AIMS, and implementing controls. This phase of your ISO 42001 checklist ends with your internal audit to assess your ISO 42001 certification readiness before moving on to external evaluations:
1. Designate a Compliance Project Leader
Select a qualified compliance leader.
Appoint a project manager with a solid understanding of AI and compliance issues. This individual will coordinate all activities related to achieving ISO 42001 certification and act as the point of communication between departments and external auditors.
2. Draft An Implementation Roadmap For AIMS
Develop a detailed project plan for your ISO 42001 process.
Solidify your project plan using the gap analysis conducted earlier as a baseline. Your plan should include deadlines, resource allocations, and every stage from the initial assessment to the final audit.
Budget appropriately.
Allocate sufficient financial and human resources to support the project. This includes funding for training, external consultants, auditing costs for certification, and technology upgrades needed to comply with ISO 42001.
*TIP: When implementing ISO 42001, you should not rely on checklists alone from external sources. Purchasing the standard should be in your budget for successful implementation.
3. Set Up The AIMS Structure
Define Your AI Management System Structure.
Set up a structure for your AIMS that integrates with existing organizational processes. The structure should support all stages of AI lifecycle management, from development to deployment and maintenance.
Document All Processes.
Make sure you are documenting everything as you work through these steps. You'll need everything from workflows, decision-making processes, and control measures documented when it comes time for your audit.
*TIP: Using a compliance automation tool at this point can be tremendously helpful. Compliance automation platforms allow you to easily organize your documentation. When it comes time for your audit, it makes your auditor's job easier and more efficient to be able to see everything clearly laid out in one central place.
4. Create Organization-Wide Awareness
Develop training programs.
Organize training sessions to improve your employees' AI and compliance knowledge base. Focus on ethical AI use, data security, and the legal implications of AI technologies.
Circulate information across the organization.
Distribute informational materials and regular updates about AIMS and its importance to encourage organization-wide understanding and engagement. Internal communications channels such as newsletters, intranets, and staff meetings are all good avenues for dissemination.
5. Apply Necessary AIMS Controls
Implement controls.
ISO 42001 controls address risk management, data protection, system reliability, and transparency.
The way controls are implemented will vary depending on your organization's industry, needs, risks, and the types of AI applications you use. (A complete control list can be found in ISO/IEC 42001:2023, Annex A).
*TIP: Consulting with a compliance expert at this step may be necessary. Many startups choose to work with a Managed Security Services Provider (MSSP) at this stage. Rhymetec's vCISO program provides hands-on managed security services, taking the complexity of compliance off your plate, and doing the readiness and audit phases for you.
Plan to regularly update control measures.
Continuous improvement is required by ISO 42001. You should plan to continuously monitor and update controls to adapt to new technologies, changes in organizational processes, and shifts in regulatory requirements.
6. Conduct Executive AIMS Evaluations As An Ongoing Piece of Your ISO 42001 Process
Organize regular review meetings.
Hold management review meetings periodically to assess the AIMS' performance. Reviews should involve top management and key stakeholders to help AI systems & applications align with broader organizational goals.
Update your executive team regularly.
The last step in this phase of your ISO 42001 checklist is to regularly update your executive team. Keep them informed about the outcomes of management reviews, including challenges, achievements, and the effectiveness of the AIMS.
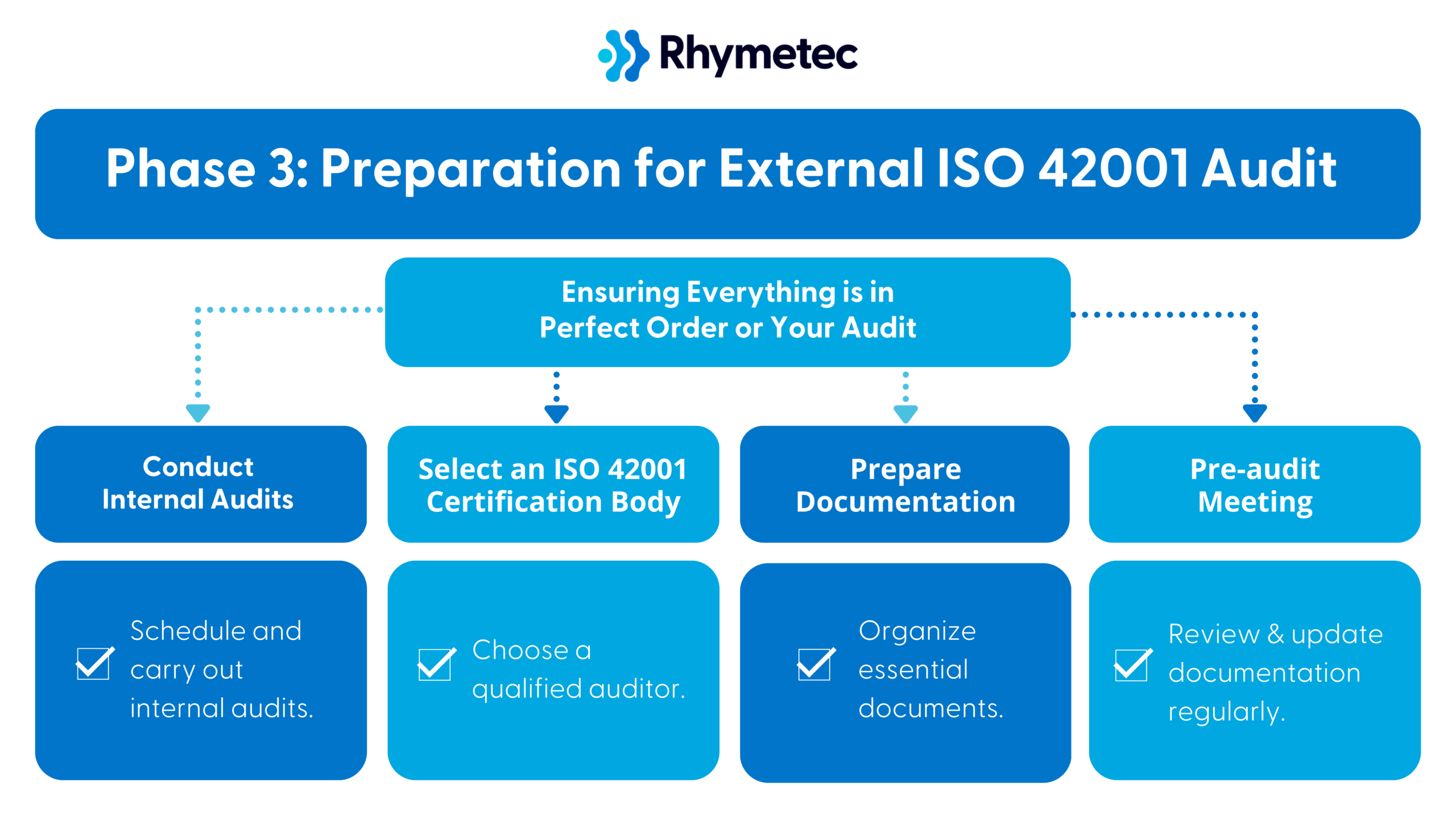
ISO 42001 Checklist Phase 3: Preparation for External ISO 42001 Audit
This stage is where you make sure everything is in perfect order for your audit.
Choosing the right auditor is critical - you want to choose a reputable certification body that will conduct a legitimate and fair audit, providing credible validation of your AIMS.
Each step in this phase is also an opportunity to solidify stakeholder confidence and demonstrate your proactive approach to responsible AI management and compliance.
1. Conduct Internal Audits
Schedule and carry out internal audits.
ISO internal audits identify any gaps in compliance and provide recommendations for improvements before your external audit. It serves as a trial run, providing insights into potential audit challenges and giving you a chance to address any issues.
2. Select an ISO 42001 Certification Body
Choose a qualified auditor.
Select an auditing firm that has been certified to offer ISO certifications and has demonstrated experience in assessing AI management systems. Your certification body must be accredited to guarantee a legitimate audit and certification.
3. Prepare Documentation
Organize essential documents.
Gather documentation that demonstrates your compliance with ISO 42001. Documents are to include policies, procedures, control implementation records, and evidence of your plans for continuous improvement efforts.
Make things as easy as possible for your auditors! Documents should be in a format that is readily available and organized for easy reference during the audit.
Review and update documentation regularly.
Regularly review your AIMS documentation to make sure it accurately reflects current AI management practices and that all modifications are recorded. Keep this documentation accessible to all relevant personnel and the auditing team.
4. Pre-audit Meeting
Set up an initial audit meeting.
Arrange a meeting with the selected certification body to discuss the audit process. Use this as an opportunity to understand the audit scope, methodology, and specific focus areas. You should also align expectations and clarify the audit schedule.
Compile key audit questions.
Beforehand, prepare a list of questions and points needing clarification. Cover logistical details, specific compliance queries, and any concerns about the AIMS implementation.
Discuss audit scope.
You'll want to clarify the detailed scope of the audit and confirm that both parties have a mutual understanding of the audit boundaries. The scope must cover all relevant areas of your AIMS.
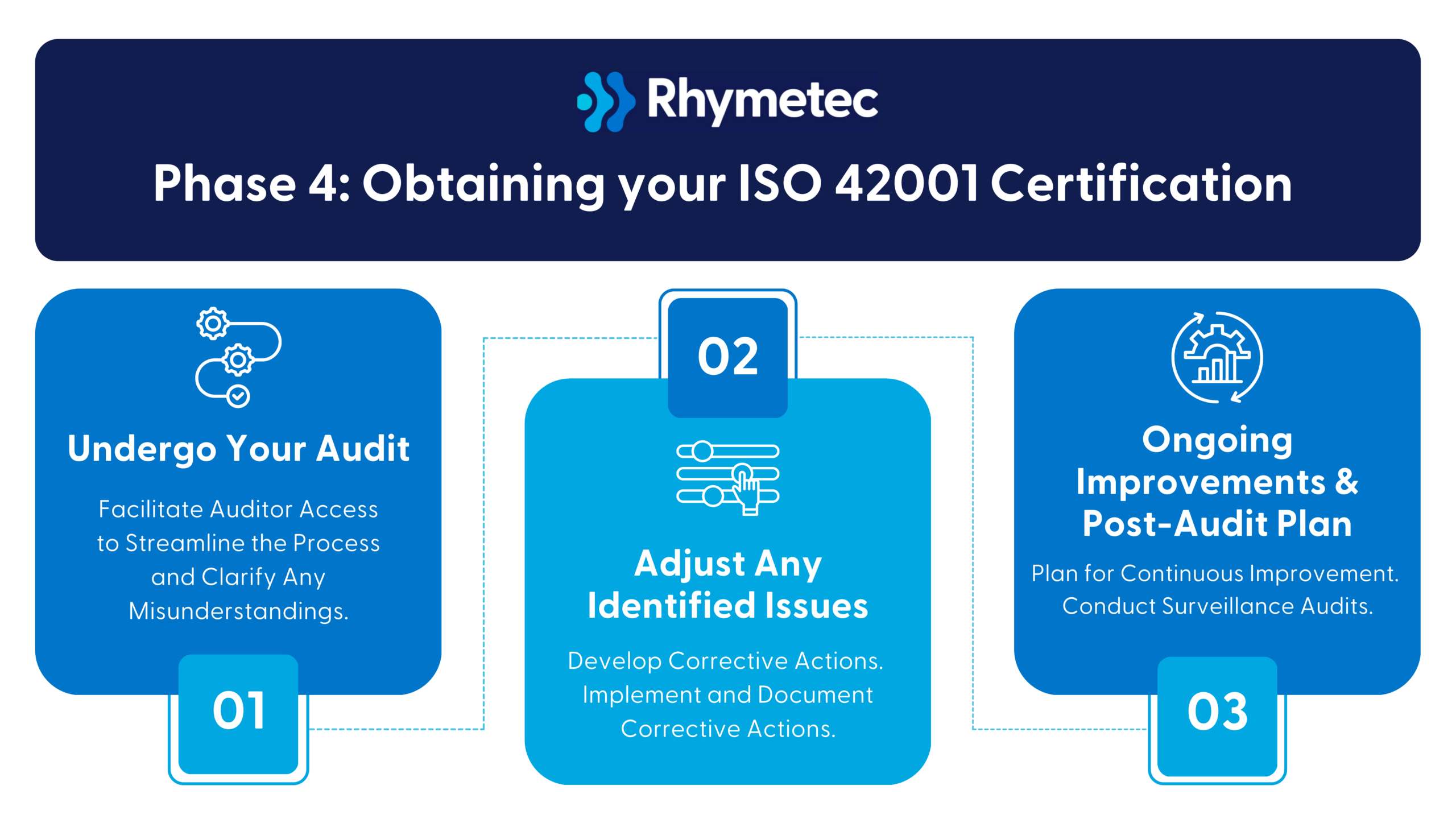
Phase 4: Obtaining your ISO 42001 Certification
This final phase is where all of your preparation pays off.
Engaging fully with auditors transforms this process from a compliance exercise to a powerful tool for improving your operations and reputation. Undergoing your audit isn't just a badge for your business to put on your website; it's a statement that you take AI risks seriously and are ahead of the curve in managing AI responsibly.
Lastly, continually improving after the audit shows you're not just "checking a box" to get through an audit. Ongoing improvements post-audit strengthen trust among clients and partners and support compliance maintenance.
1. Undergo Your Audit
Facilitate Auditor Access.
Auditors need to have full access to all relevant sites, personnel, and documentation. Designate a team member to serve as a point of contact and participate in discussions with auditors to streamline the process and clarify any misunderstandings.
2. Address Any Identified Issues
Develop Corrective Actions.
Promptly create action plans for any non-compliance issues identified during the audit. Assign clear responsibilities and timelines for these actions.
Implement and Document Corrective Actions.
Execute the necessary corrective measures and document the processes. You will need this documentation during follow-up audits.
3. Ongoing Improvements & Post-Audit Plan
Plan for Continuous Improvement.
Develop a plan for continuous improvement based on audit findings.
Your post-audit plan should include updating training programs and communication with employees to address any changes. Schedule regular intervals to review the AIMS and identify opportunities to improve.
Conduct Surveillance Audits In Preparation to Re-certify Every 3 Years.
Lastly, keep in mind you will need future surveillance audits as part of your ongoing ISO 42001 process:
ISO 42001 requires recertification every 3 years to remain compliant. Surveillance audits are needed in between to ensure your organization is ready for the next official audit.
Immediate Benefits After Completing Your ISO 42001 Checklist
After you've completed all items in your ISO 42001 checklist and have your certification in hand, you will see a number of immediate benefits:
You will now be able to communicate, through verified third-party documentation, to your prospects and customers that your AI use follows the highest industry standards. You can use your certification to assuage any concerns your clients and prospects may have about AI. Being able to show them your documentation increases trust and can shorten your sales cycle. This is especially important given that there is growing concern over generative AI security risks.
Additionally, you will have peace of mind knowing that your risk is substantially reduced. The roadmap you now have for the strategic use of AI will serve as a business enabler as you continue to expand your AI offerings and break into new marketplaces.
For more information, check out our ISO 42001 Compliance FAQ for the most common questions our team at Rhymetec sees about ISO 42001 (Who Needs ISO 42001?, How Different Is ISO 42001 Vs. ISO 27001?, How Much Does ISO 42001 Certification Cost?, How Long Does ISO 42001 Certification Take?, and more), or contact our team today:
About Rhymetec
Our mission is to make cutting-edge cybersecurity available to SaaS companies and startups. We've worked with hundreds of companies to provide practical security solutions tailored to their needs, enabling them to be secure and compliant while balancing security with budget. We enable our clients to outsource the complexity of security and focus on what really matters – their business.
If your organization is interested in exploring compliance with AI standards, we now offer ISO/IEC 42001 certification readiness and maintenance services and are happy to answer any questions you may have on the ISO 42001 process.
Interested in reading more? Check out more content on our blog.